Enhancing stroke disease classification through machine learning models via a novel voting system by feature selection techniques
- PMID: 39787105
- PMCID: PMC11717207
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312914
Enhancing stroke disease classification through machine learning models via a novel voting system by feature selection techniques
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Enhancing stroke disease classification through machine learning models via a novel voting system by feature selection techniques.PLoS One. 2025 May 20;20(5):e0324683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324683. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40392761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
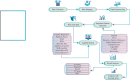
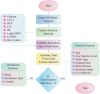
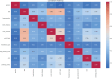
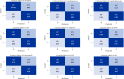
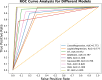
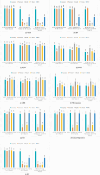
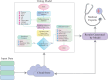
Heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide, necessitating the development of accurate and reliable predictive models to facilitate early detection and intervention. While state of the art work has focused on various machine learning approaches for predicting heart disease, but they could not able to achieve remarkable accuracy. In response to this need, we applied nine machine learning algorithms XGBoost, logistic regression, decision tree, random forest, k-nearest neighbors (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), gaussian naïve bayes (NB gaussian), adaptive boosting, and linear regression to predict heart disease based on a range of physiological indicators. Our approach involved feature selection techniques to identify the most relevant predictors, aimed at refining the models to enhance both performance and interpretability. The models were trained, incorporating processes such as grid search hyperparameter tuning, and cross-validation to minimize overfitting. Additionally, we have developed a novel voting system with feature selection techniques to advance heart disease classification. Furthermore, we have evaluated the models using key performance metrics including accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC). Among the models, XGBoost demonstrated exceptional performance, achieving 99% accuracy, precision, F1-Score, 98% recall, and 100% ROC AUC. This study offers a promising approach to early heart disease diagnosis and preventive healthcare.
Copyright: © 2025 Hasan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of an efficient novel method for coronary artery disease prediction using machine learning and deep learning techniques.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(6):4545-4569. doi: 10.3233/THC-240740. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 39031414 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective study using machine learning to develop predictive model to identify rotavirus-associated acute gastroenteritis in children.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 14;13:e19025. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19025. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40247842 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and feature selection of low birth weight using machine learning algorithms.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Oct 12;43(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00647-8. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39396025 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning algorithms for predicting COVID-19 mortality in Ethiopia.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 28;24(1):1728. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19196-0. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38943093 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Binary Classifiers for Cardiovascular Disease Prediction: Enhancing Early Diagnostic Capabilities.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Dec 9;11(12):396. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11120396. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39728286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retraction: Enhancing stroke disease classification through machine learning models via a novel voting system by feature selection techniques.PLoS One. 2025 May 20;20(5):e0324683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324683. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40392761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- “Stroke: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Types,” Cleveland Clinic. Accessed: Sep. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/5601-stroke.
-
- “Cardiovascular diseases.” Accessed: Sep. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases.
-
- Greenfield D. M. and Snowden J. A., “Cardiovascular Diseases and Metabolic Syndrome,” in The EBMT Handbook: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies, 7th ed., Carreras E., Dufour C., Mohty M., and Kröger N., Eds., Cham (CH): Springer, 2019. Accessed: Sep. 04, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554003/. - PubMed
-
- Chen A. H., Huang S. Y., Hong P. S., Cheng C. H., and Lin E. J., “HDPS: Heart disease prediction system,” in 2011 Computing in Cardiology, Sep. 2011, pp. 557–560. Accessed: Dec. 21, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6164626/references#references.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

