Let-7b-5p sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through Aurora Kinase B
- PMID: 39787178
- PMCID: PMC11717257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307420
Let-7b-5p sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through Aurora Kinase B
Abstract
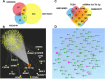
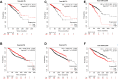
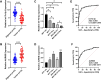
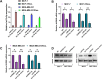
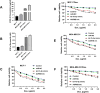
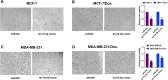
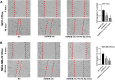
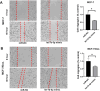
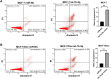
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that regulate the expression level of the target genes in the cell. Breast cancer is responsible for the majority of cancer-related deaths among women globally. It has been proven that deregulated miRNAs may play an essential role in the progression of breast cancer. It has been shown in many cancers, including breast cancer, that aberrant expression of miRNAs may be associated with drug resistance. This study investigated the effect of let-7b-5p, detected by bioinformatics methods, on Dox resistance through the Aurora Kinase B (AURKB) gene. In silico analysis using publicly available miRNA expression, GEO datasets revealed that let-7b-5p significantly downregulated in BC. Further in silico studies revealed that of the genes among the potential targets of let-7b-5p, AURKB was the most negatively correlated and may be closely associated with Dox resistance. Expression analysis via quantitative PCR confirmed that let-7b-5p was downregulated and AURKB was upregulated in breast cancer tissue samples. Later, functional studies conducted with MCF-10A, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines demonstrated that let-7b-5p inhibits cancer cells through AURKB and sensitizes them to Dox resistance. In conclusion, it has been shown that the let-7b-5p/AURKB axis may be significant in breast cancer progression and the disruption in this axis may contribute to the trigger of Dox resistance.
Copyright: © 2025 Kaya et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: -The corresponding author, Dr Zeyneb Kurt, is a member of the editorial board for the PLOS ONE journal. -The rest of the authors have declared that no other competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA let-7b regulates genomic balance by targeting Aurora B kinase.Mol Oncol. 2015 Jun;9(6):1056-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25682900 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-192-5p impacts the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin via targeting peptidylprolyl isomerase A.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 Jan;35(1):17-23. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12004. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30844143 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated let-7b-5p represses glycolysis metabolism by targeting AURKB in asthenozoospermia.Gene. 2018 Jul 15;663:83-87. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.022. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29653228
-
Long non-coding RNA X-inactive-specific transcript contributes to cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by sponging miR-let-7b.Anticancer Drugs. 2020 Nov;31(10):1018-1025. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000942. Anticancer Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33009035
-
MicroRNA-205-5p inhibits the growth and migration of breast cancer through targeting Wnt/β-catenin co-receptor LRP6 and interacting with lncRNAs.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2117-2129. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05136-4. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39461917 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

