Is preoperative imaging of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer necessary? A retrospective case control study
- PMID: 39787816
- PMCID: PMC11763842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103856
Is preoperative imaging of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer necessary? A retrospective case control study
Abstract
Objective: The necessity of preoperative lymphoscintigraphy before intraoperative sentinel lymph node (SLN) identification is still unclear. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the impact of SLN imaging on intraoperative SLN detection in breast cancer patients.
Methods: Retrospective, comparative, single center study of patients with breast cancer stage pT1 and pT2 who underwent axillary staging. Group 1 included patients who underwent SLN extirpation without preoperative SLN imaging, and Group 2 included patients who underwent SLN imaging prior to surgery. Differences between groups were analyzed using T-test and chi-square test.
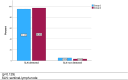
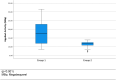
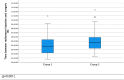
Results: 926 (mean age: 61.45 years) patients received subdermal injection of radiolabeled nanocolloids between tumor and axilla. SLN was identified intraoperatively in 473 of 498 patients (94.98 %) in group 1, and in 415 of 428 patients (96.96 %) in group 2 (p = 0.129). Lymphoscintigraphy detected SLN in 407 of 428 (95.09 %) patients in group 2. Due to the additional SLN imaging in group 2, the time between radiotracer injection and start of surgery was significantly prolonged (p < 0.001). A reduction of applied activity from a median of 18 MBq in group 1 to a median of 12 MBq in group 2 had no negative effect on the SLN identification.
Conclusion: Subdermal injection of radiolabeled nanocolloids between tumor and axilla allowed high intraoperative detection of SLN. Preoperative SLN imaging had no significant impact on the intraoperative detection but is a time-consuming and resource-intensive procedure. Prospective studies might provide further evidence to omit preoperative SLN imaging in patients with T1-2 invasive breast cancer and clinically negative axilla.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Scintigraphy; Sentinel lymph node.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, International Agency for Research on Cancer Incidence of cancer, Females, in 2022. 2022. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en/dataviz/pie?mode=cancer&group_populations=1... [Available from:
-
- The American Society of Breast Surgeons Performance and practice guidelines for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients: the American society of breast surgeons. 2014. https://www.breastsurgeons.org/docs/statements/Performance-and-Practice-... [Available from:
-
- Goyal A., Newcombe R.G., Mansel R.E., Chetty U., Ell P., Fallowfield L., et al. Role of routine preoperative lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41(2):238–243. - PubMed
-
- Sun X., Liu J.J., Wang Y.S., Wang L., Yang G.R., Zhou Z.B., et al. Roles of preoperative lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40(8):722–725. - PubMed
-
- Giammarile F., Alazraki N., Aarsvold J.N., Audisio R.A., Glass E., Grant S.F., et al. The EANM and SNMMI practice guideline for lymphoscintigraphy and sentinel node localization in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2013;40(12):1932–1947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical