Moringa oleifera L. Nanosuspension Extract Administration Affects Heat Shock Protein-10 and -70 under Orthodontics Mechanical Force In Vivo
- PMID: 39788532
- PMCID: PMC12020578
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-1791937
Moringa oleifera L. Nanosuspension Extract Administration Affects Heat Shock Protein-10 and -70 under Orthodontics Mechanical Force In Vivo
Abstract
Objective: The mechanical stimulation known as orthodontic mechanical force (OMF) causes biological reactions in orthodontic tooth movement (OTM). Heat shock protein-70 (HSP-70) needs pro-inflammatory cytokines to trigger bone resorption in OTM; nevertheless, heat shock protein-10 (HSP-10), a "Alarmin" cytokine, should control these pro-inflammatory cytokines to get the best alveolar bone remodeling (ABR). Moringa oleifera L. nanosuspension extract (MONE) has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and ABR-stimulating properties. The aim of the study was to examine in vivo HSP-10 and HSP-70 expressions under OMF following MONE application in Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus).
Material and methods: A total of 36 Wistar rats (R. norvegicus) were split up into eight groups: one for treatment (OMF + MONE) and one for control (OMF + MONE administration for days 1, 7, 14, and 21). By employing nickel-titanium coil springs and using 10 g of light force per millimeter to implant the orthodontic device, the OMF was completed. According to the day of observation, all of the samples were sacrificed. To perform an immunohistochemistry investigation, the premaxilla of the sample was isolated. Tukey's Honest Significant Different (HSD) test (p < 0.05) was performed after an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) analysis of the data.
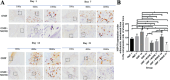
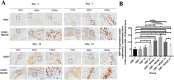
Results: In both the OMF and MONE groups, HSP-70 peaked on day 14 and began to fall on day 21. HSP-10 peaked on day 21, but along with MONE, it also began to progressively decline on days 14 and 21, with significant differences (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: According to immunohistochemistry evidence, postadministration of MONE markedly elevated HSP-10 but lowered HSP-70 expression in the alveolar bone of Wistar rats under OMF.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Lombardo G, Vena F, Negri P et al. Worldwide prevalence of malocclusion in the different stages of dentition: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2020;21(02):115–122. - PubMed
-
- Inchingolo F, Inchingolo A M, Palmieri G et al. Root resorption during orthodontic treatment with clear aligners vs. fixed appliances—a systematic review. Appl Sci (Basel) 2024;14(02):690. doi: 10.3390/app14020690. - DOI
-
- Toyokawa-Sperandio K C, Conti A CCF, Fernandes T MF, Almeida-Pedrin R R, Almeida M R, Oltramari P VP. External apical root resorption 6 months after initiation of orthodontic treatment: a randomized clinical trial comparing fixed appliances and orthodontic aligners. Korean J Orthod. 2021;51(05):329–336. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thulasidharan M U, Vijayaraghavan N, Krishnan V. Heat shock protein 70 and the extent of nuclear damage in periodontal ligament compression side cells with orthodontic force application—an ex-vivo evaluation. Int Orthod. 2021;19(03):487–493. - PubMed
-
- Bozkaya E, Canigur Bavbek N, Isler S C et al. Evaluation of heat shock protein 70 and toll-like receptor 4 expression in gingival crevicular fluid in response to orthodontic forces. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(11):6455–6464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

