Mitochondrial diseases: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic advances
- PMID: 39788934
- PMCID: PMC11724432
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-02044-3
Mitochondrial diseases: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic advances
Abstract
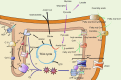
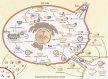
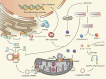
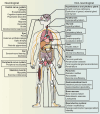
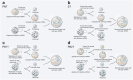
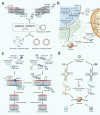
Mitochondria are essential for cellular function and viability, serving as central hubs of metabolism and signaling. They possess various metabolic and quality control mechanisms crucial for maintaining normal cellular activities. Mitochondrial genetic disorders can arise from a wide range of mutations in either mitochondrial or nuclear DNA, which encode mitochondrial proteins or other contents. These genetic defects can lead to a breakdown of mitochondrial function and metabolism, such as the collapse of oxidative phosphorylation, one of the mitochondria's most critical functions. Mitochondrial diseases, a common group of genetic disorders, are characterized by significant phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity. Clinical symptoms can manifest in various systems and organs throughout the body, with differing degrees and forms of severity. The complexity of the relationship between mitochondria and mitochondrial diseases results in an inadequate understanding of the genotype-phenotype correlation of these diseases, historically making diagnosis and treatment challenging and often leading to unsatisfactory clinical outcomes. However, recent advancements in research and technology have significantly improved our understanding and management of these conditions. Clinical translations of mitochondria-related therapies are actively progressing. This review focuses on the physiological mechanisms of mitochondria, the pathogenesis of mitochondrial diseases, and potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Additionally, this review discusses future perspectives on mitochondrial genetic diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

