DCAF13-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of RNA polymerase I promotes uncontrolled proliferation in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39788980
- PMCID: PMC11718263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55851-9
DCAF13-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of RNA polymerase I promotes uncontrolled proliferation in Breast Cancer
Abstract
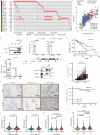
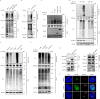
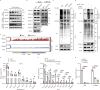
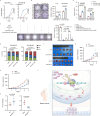
Hyperactivation of ribosome biogenesis (RiBi) drives cancer progression, yet the role of RiBi-associated proteins (RiBPs) in breast cancer (BC) is underexplored. In this study, we perform a comprehensive multi-omics analysis and reveal that assembly and maturation factors (AMFs), a subclass of RiBPs, are upregulated at both RNA and protein levels in BC, correlating with poor patient outcomes. In contrast, ribosomal proteins (RPs) do not show systematic upregulation across various cancers, including BC. We further demonstrate that the oncogenic activation of a top AMF candidate in BC, DCAF13, enhances Pol I transcription and promotes proliferation in BC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, DCAF13 promotes Pol I transcription activity by facilitating the K63-linked ubiquitination of RPA194. This process stimulates global protein synthesis and cell growth. Our findings uncover a modification of RPA194 that regulates Pol I activity; this modification is dysregulated in BC, contributing to cancer progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82073067/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81872140/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2022B1515020100/Guangdong Science and Technology Department (Science and Technology Department, Guangdong Province)
- 2019B020226003/Guangdong Science and Technology Department (Science and Technology Department, Guangdong Province)
- 2023B1212060013/Guangdong Science and Technology Department (Science and Technology Department, Guangdong Province)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

