Mapping mitochondrial morphology and function: COX-SBFSEM reveals patterns in mitochondrial disease
- PMID: 39789156
- PMCID: PMC11718190
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07389-7
Mapping mitochondrial morphology and function: COX-SBFSEM reveals patterns in mitochondrial disease
Abstract
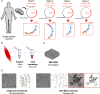
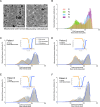
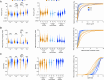
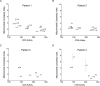
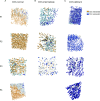
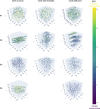
Mitochondria play a crucial role in maintaining cellular health. It is interesting that the shape of mitochondria can vary depending on the type of cell, mitochondrial function, and other cellular conditions. However, there are limited studies that link functional assessment with mitochondrial morphology evaluation at high magnification, even fewer that do so in situ and none in human muscle biopsies. Therefore, we have developed a method which combines functional assessment of mitochondria through Cytochrome c Oxidase (COX) histochemistry, with a 3D electron microscopy (EM) technique, serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBFSEM). Here we apply COX-SBFSEM to muscle samples from patients with single, large-scale mtDNA deletions, a cause of mitochondrial disease. These deletions cause oxidative phosphorylation deficiency, which can be observed through changes in COX activity. One of the main advantages of combining 3D-EM with the COX reaction is the ability to look at how per-mitochondrion oxidative phosphorylation status is spatially distributed within muscle fibres. Here we show a robust spatial pattern in COX-positive and intermediate-fibres and that the spatial pattern is less clear in COX-deficient fibres.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JF is an employee of Amazentis. DMT is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Khondrion BV and Pretzel therapeutics. DMT does consultancy work for Reneo Pharma, Droia NV, IMEL Biotherapeutics and Precision Biosciences. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ogata, T. & Yamasaki, Y. Scanning electron-microscopic studies on the three-dimensional structure of mitochondria in the mammalian red, white and intermediate muscle fibers. Cell Tissue Res.241, 251–256 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Picard, M., Hepple, R. T. & Burelle, Y. Mitochondrial functional specialization in glycolytic and oxidative muscle fibers: tailoring the organelle for optimal function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol.302, C629–C641 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Ferreira, R. et al. Subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar mitochondria proteome differences disclose functional specializations in skeletal muscle. Proteomics10, 3142–3154 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

