Overlooked and underpowered: a meta-research addressing sample size in radiomics prediction models for binary outcomes
- PMID: 39789271
- PMCID: PMC11835977
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-11331-0
Overlooked and underpowered: a meta-research addressing sample size in radiomics prediction models for binary outcomes
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate how studies determine the sample size when developing radiomics prediction models for binary outcomes, and whether the sample size meets the estimates obtained by using established criteria.
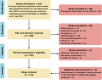
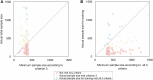
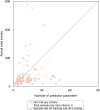
Methods: We identified radiomics studies that were published from 01 January 2023 to 31 December 2023 in seven leading peer-reviewed radiological journals. We reviewed the sample size justification methods, and actual sample size used. We calculated and compared the actual sample size used to the estimates obtained by using three established criteria proposed by Riley et al. We investigated which characteristics factors were associated with the sufficient sample size that meets the estimates obtained by using established criteria proposed by Riley et al. RESULTS: We included 116 studies. Eleven out of one hundred sixteen studies justified the sample size, in which 6/11 performed a priori sample size calculation. The median (first and third quartile, Q1, Q3) of the total sample size is 223 (130, 463), and those of sample size for training are 150 (90, 288). The median (Q1, Q3) difference between total sample size and minimum sample size according to established criteria are -100 (-216, 183), and those differences between total sample size and a more restrictive approach based on established criteria are -268 (-427, -157). The presence of external testing and the specialty of the topic were associated with sufficient sample size.
Conclusion: Radiomics studies are often designed without sample size justification, whose sample size may be too small to avoid overfitting. Sample size justification is encouraged when developing a radiomics model.
Key points: Question Sample size justification is critical to help minimize overfitting in developing a radiomics model, but is overlooked and underpowered in radiomics research. Findings Few of the radiomics models justified, calculated, or reported their sample size, and most of them did not meet the recent formal sample size criteria. Clinical relevance Radiomics models are often designed without sample size justification. Consequently, many models are too small to avoid overfitting. It should be encouraged to justify, perform, and report the considerations on sample size when developing radiomics models.
Keywords: Methodology; Prediction model; Radiomics; Sample size.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Guarantor: The scientific guarantor of this publication is Prof. Weiwu Yao from the Department of Imaging, Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. Conflict of interest: J.Z. acknowledges his position as a member of the Scientific Editorial Board of European Radiology, American Journal of Roentgenology, and BMC Medical Imaging. He has therefore not taken part in the review or selection process of this paper. R.J., from a commercial company, SciClone Pharmaceuticals (Holdings) Limited, is an expert in pharmacovigilance doing adverse drug reaction surveillance of anticancer drugs, without any payment and personal concern regarding this study. Y.S. and M.L., both from a commercial company, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., are an MR collaboration scientist and technicians doing technical support under Siemens collaboration regulation, without any payment and personal concern regarding this study. All other authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. Statistics and biometry: One of the authors is an expert in statistics and biometry, who kindly provided statistical advice. Informed consent: Written informed consent was not required for this study because no human or animal subjects have been included in this study. Ethical approval: Ethical approval was not required for this study because no human or animal subjects have been included in this study. Study subjects or cohorts overlap: The abstract of this article entitled “Overlooked and underpowered: a meta-research study addressing sample size in radiomics research” (#10163) has been accepted as an oral presentation at the European Congress of Radiology 2025, February 26 - March 02, 2025, Vienna, Austria. The presenting author of this abstract is Dr. Jingyu Zhong. Methodology: Experimental Retrospective Performed at one institution
Figures
Comment in
-
Sample size estimation for radiomics studies: an overlooked problem.Eur Radiol. 2025 Sep;35(9):5226-5227. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11538-9. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40140080 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82302183/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82471935/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82271934/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20244Y0214/Research Found of Health Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 22YF1442400/Yangfan Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 2023QN01/Research Found of Health Commission of Changing District, Shanghai Municipality
- 2024JZWC-ZDA03/Laboratory Open Fund of Key Technology and Materials in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- 2024JZWC-YBA07/Laboratory Open Fund of Key Technology and Materials in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- TRKYRC-XX202204/Research Fund of Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
- TRYXJH28/Research Fund of Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
- TRYJ2021JC06/Research Fund of Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
- TRGG202101/Research Fund of Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
- TRYXJH18/Research Fund of Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

