A scalable variational inference approach for increased mixed-model association power
- PMID: 39789286
- PMCID: PMC11821521
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-02044-7
A scalable variational inference approach for increased mixed-model association power
Abstract
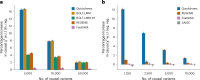
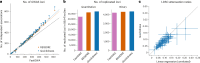
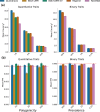
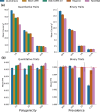
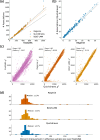
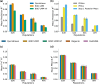
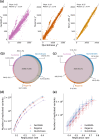
The rapid growth of modern biobanks is creating new opportunities for large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and the analysis of complex traits. However, performing GWASs on millions of samples often leads to trade-offs between computational efficiency and statistical power, reducing the benefits of large-scale data collection efforts. We developed Quickdraws, a method that increases association power in quantitative and binary traits without sacrificing computational efficiency, leveraging a spike-and-slab prior on variant effects, stochastic variational inference and graphics processing unit acceleration. We applied Quickdraws to 79 quantitative and 50 binary traits in 405,088 UK Biobank samples, identifying 4.97% and 3.25% more associations than REGENIE and 22.71% and 7.07% more than FastGWA. Quickdraws had costs comparable to REGENIE, FastGWA and SAIGE on the UK Biobank Research Analysis Platform service, while being substantially faster than BOLT-LMM. These results highlight the promise of leveraging machine learning techniques for scalable GWASs without sacrificing power or robustness.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 108861/Z/15/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 850869/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- EP/L016044/1/RCUK | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

