Right Coronary Artery Dissection After Ross Procedure
- PMID: 39790517
- PMCID: PMC11708567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atssr.2022.10.016
Right Coronary Artery Dissection After Ross Procedure
Abstract
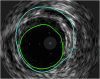
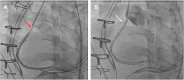
The Ross procedure is a surgical option for the treatment of aortic valve stenosis that is performed in a select subset of patients. This case report highlights the rare complication of a coronary artery dissection that occurred in the early postoperative period after a Ross procedure. The importance of timely recognition, swift intervention, and multidisciplinary team collaboration is discussed in the postoperative management of this complex cardiac surgery patient.
Figures