Device-assisted strategies for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier to treat glioblastoma
- PMID: 39790893
- PMCID: PMC11706785
- DOI: 10.1038/s43246-024-00721-y
Device-assisted strategies for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier to treat glioblastoma
Abstract
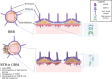
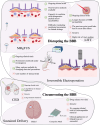
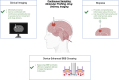
The blood-brain barrier, essential for protecting the central nervous system, also restricts drug delivery to this region. Thus, delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier is an active research area in immunology, oncology, and neurology; moreover, novel methods are urgently needed to expand therapeutic options for central nervous system pathologies. While previous strategies have focused on small molecules that modulate blood-brain barrier permeability or penetrate the barrier, there is an increased focus on biomedical devices-external or implanted-for improving drug delivery. Here, we review device-assisted drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier, emphasizing its application in glioblastoma, an aggressively malignant primary brain cancer in which the blood-brain barrier plays a central role. We examine the blood-brain barrier and its features in glioblastoma, emerging models for studying the blood-brain barrier, and device-assisted methods for crossing the blood-brain barrier. We conclude by presenting methods to monitor the blood-brain barrier and paradigms for combined cross-BBB drug delivery.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Blood-brain barrier; CNS cancer; Translational research.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Terstappen, G. C., Meyer, A. H., Bell, R. D. & Zhang, W. Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.20, 362–383 (2021). This article provides a comprehensive review of the non-invasive and pharmacological-based methods for drug delivery to the CNS. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
