Cullin-5 controls the number of megakaryocyte-committed stem cells to prevent thrombocytosis in mice
- PMID: 39791603
- PMCID: PMC11923429
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2024025406
Cullin-5 controls the number of megakaryocyte-committed stem cells to prevent thrombocytosis in mice
Abstract
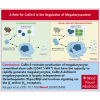
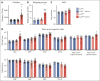
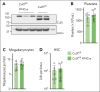
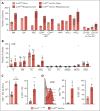
Cullin-5 (Cul5) coordinates the assembly of cullin-RING-E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes that include the suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-box-containing proteins. The SOCS-box proteins function to recruit specific substrates to the complex for ubiquitination and degradation. In hematopoiesis, SOCS-box proteins are best known for regulating the actions of cytokines that utilize the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. However, the roles of most SOCS-box proteins have not been studied in physiological contexts and any actions for Cul5/SOCS complexes in signaling by several hematopoietic cytokines, including thrombopoietin (TPO) and interleukin-3 (IL-3), remain unknown. To define additional potential roles for Cul5/SOCS complexes, we generated mice lacking Cul5 in hematopoiesis; the absence of Cul5 is predicted to impair the SOCS-box-dependent actions of all proteins that contain this motif. Here, we show that Cul5-deficient mice develop excess megakaryopoiesis and thrombocytosis revealing a novel mechanism of negative regulation of megakaryocyte-committed stem cells, a distinct population within the hematopoietic stem cell pool that have been shown to rapidly, perhaps directly, generate megakaryocytes, and which are produced in excess in the absence of Cul5. Cul5-deficient megakaryopoiesis is distinctive in being largely independent of TPO/myeloproliferative leukemia protein and involves signaling via the β-common and/or β-IL-3 receptors, with evidence of deregulated responses to IL-3. This process is independent of the interferon-α/β receptor, previously implicated in inflammation-induced activation of stem-like megakaryocyte progenitor cells.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosures: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
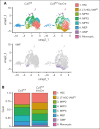
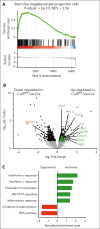
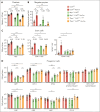
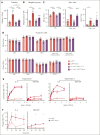
Comment in
-
Cullin' the herd: Cul5 limits megakaryocyte-biased HSCs.Blood. 2025 Mar 6;145(10):996-998. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024027680. Blood. 2025. PMID: 40048228 No abstract available.
References
-
- Linossi EM, Nicholson SE. The SOCS box-adapting proteins for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. IUBMB Life. 2012;64(4):316–323. - PubMed
-
- Alexander WS, Starr R, Fenner JE, et al. SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon gamma signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions of this cytokine. Cell. 1999;98(5):597–608. - PubMed
-
- Chong MM, Cornish AL, Darwiche R, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 is a critical regulator of interleukin-7-dependent CD8+ T cell differentiation. Immunity. 2003;18(4):475–487. - PubMed
-
- Cornish AL, Chong MM, Davey GM, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 regulates signaling in response to interleukin-2 and other gamma c-dependent cytokines in peripheral T cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(25):22755–22761. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

