Nuclear N-WASP Induces Actin Polymerization in the Nucleus with Cortactin as an Essential Factor
- PMID: 39791760
- PMCID: PMC11720165
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14010059
Nuclear N-WASP Induces Actin Polymerization in the Nucleus with Cortactin as an Essential Factor
Abstract
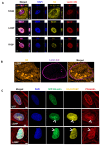
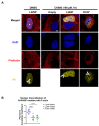
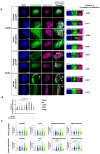
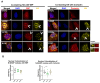
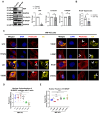
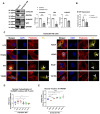
Nuclear actin polymerization was reported to control different nuclear processes, but its regulation is poorly understood. Here, we show that N-WASP can trigger the formation of nuclear N-WASP/F-actin nodules. While a cancer hotspot mutant of N-WASP lacking the VCA domain (V418fs) had a dominant negative function on nuclear F-actin, an even shorter truncation mutant found in melanoma (R128*) strongly promoted nuclear actin polymerization. Nuclear localization of N-WASP was not regulated by the cell cycle and increasing nuclear F-actin formation by N-WASP had no obvious influence on replication. However, nuclear N-WASP/F-actin nodules colocalized partially with RNA Pol II clusters. N-WASP-dependent actin polymerization promoted the maturation of RNA Pol II clusters, with the short truncation mutant R128* unexpectedly showing the strongest effect. Nuclear N-WASP nodules including V418fs colocalized with WIP and cortactin. Importantly, cortactin binding was essential but not sufficient for F-actin formation, while WIP binding was required for actin polymerization by R128*. These data reveal a cortactin-dependent role for N-WASP in the regulation of nuclear F-actin and indicate contrasting nuclear effects for N-WASP mutants found in cancer.
Keywords: N-WASP; cortactin; nuclear F-actin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Snapper S.B., Takeshima F., Antón I., Liu C.H., Thomas S.M., Nguyen D., Dudley D., Fraser H., Purich D., Lopez-Ilasaca M., et al. N-WASP deficiency reveals distinct pathways for cell surface projections and microbial actin-based motility. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:897–904. doi: 10.1038/ncb1001-897. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

