Anion Transport by Bambusuril-Bile Acid Conjugates: Drastic Effect of the Cholesterol Content
- PMID: 39791967
- PMCID: PMC11848992
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202424754
Anion Transport by Bambusuril-Bile Acid Conjugates: Drastic Effect of the Cholesterol Content
Abstract
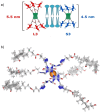
Artificial anion transporters offer a potential way to treat deficiencies in cellular anion transport of genetic origins. In contrast to the large variety of mobile anion carriers and self-assembled anion channels reported, unimolecular anion channels are less investigated. Herein, we present a unique example of a unimolecular anion channel based on a bambusuril (BU) macrocycle, a well-established anion receptor. The BU structure was expanded by appending various bile acid residues allowing a single molecule to span the membrane. Chloride transport mediated by BUs through lipid bilayers was investigated in liposomes and these studies revealed a surprisingly high dependence of the anion transport activity on the cholesterol content in the liposomal membrane.
Keywords: Anion Channels; Anion transport; Bambusurils; Macrocycles; Supramolecular Chemistry.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ashcroft F. M., Ion Channels Dis., (Ed.: Ashcroft F. M.), Academic Press, San Diego, 2000, pp. 185–198.
-
- Jentsch T. J., Stein V., Weinreich F., Zdebik A. A., Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 503–568. - PubMed
-
- Dworakowska B., Dolowy K., Acta Biochim. Pol. 2000, 47, 685–703. - PubMed
-
- Hille B., Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

