Metformin Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Preserving Mitochondrial Dynamics Balance and Calcium Homeostasis
- PMID: 39792339
- PMCID: PMC11985558
- DOI: 10.1007/s12010-024-05141-9
Metformin Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Preserving Mitochondrial Dynamics Balance and Calcium Homeostasis
Abstract
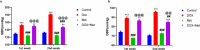
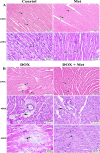
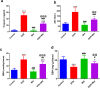
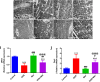
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic medication for treating malignancies, although its cardiotoxicity limits its use. There is growing evidence that alteration of the mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamic processes accompanied by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and alteration of calcium Ca2+ homeostasis are potential underlying mechanisms of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC). Metformin (Met) is an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator that has antioxidant properties and cardioprotective effects. The purpose of the study is to assess Met's possible cardioprotective benefits against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. The study included 32 adult male rats. They were randomly divided into four groups: administered saline, DOX, Met, or DOX combined with Met respectively. Heart tissues were used for biochemical assays that measured oxidative stress markers, malondialdehyde (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH), mitochondrial dynamics markers, optic atrophy-1(OPA-1) and dynamin-1-like protein (Drp1), calcineurin and caspase-3. Serum levels of myocardial injury markers, cardiac troponin I (cTn-I), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), were also measured. The results revealed that DOX intoxication was associated with a significant increase in the levels of serum cTn-I and AST, increased cardiac MDA level, increased cardiac Drp1, calcineurin, and caspase-3 expressions, as well as reduced cardiac GSH level and cardiac OPA-1 expression. On the other hand, Met treatment significantly reduced DIC by decreasing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and improving mitochondrial and calcium balance. Finally, this study shows that Met may be able to protect the heart from damage caused by DOX by working as an antioxidant and anti-apoptotic agent and keeping the balance of calcium and mitochondria.
Keywords: Calcineurin; Cardiotoxicity; Doxorubicin; Metformin; Mitochondrial dynamics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: This study was performed according to the principles and guidelines given by the Animal Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University (26/6/2023, IRB local approval number 04–2023-300201). Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

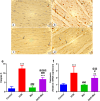
References
-
- Cardinale, D., Colombo, A., Bacchiani, G., Tedeschi, I., Meroni, C. A., Veglia, F., Civelli, M., Lamantia, G., Colombo, N., & Curigliano, G. (2015). Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation,131, 1981–1988. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

