Structural insight into sodium ion pathway in the bacterial flagellar stator from marine Vibrio
- PMID: 39793043
- PMCID: PMC11725901
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2415713122
Structural insight into sodium ion pathway in the bacterial flagellar stator from marine Vibrio
Abstract
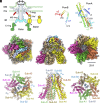
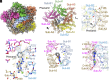
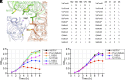
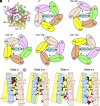
Many bacteria swim in liquid or swarm on surface using the flagellum rotated by a motor driven by specific ion flow. The motor consists of the rotor and stator, and the stator converts the energy of ion flow to mechanical rotation. However, the ion pathway and the mechanism of stator rotation coupled with specific ion flow are still obscure. Here, we determined the structures of the sodium-driven stator of Vibrio, namely PomAB, in the presence and absence of sodium ions and the structure with its specific inhibitor, phenamil, by cryo-electron microscopy. The structures and following functional analysis revealed the sodium ion pathway, the mechanism of ion selectivity, and the inhibition mechanism by phenamil. We propose a model of sodium ion flow coupled with the stator rotation based on the structures. This work provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of ion specificity and conversion of the electrochemical potential into mechanical functions.
Keywords: CryoEM; bacterial flagellum; ion-driven motor; motility; stator.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Berg H., The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 19–54 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Minamino T., Imada K., The bacterial flagellar motor and its structural diversity. Trends Microbiol. 23, 267–274 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Blair D. F., Flagellar movement driven by proton translocation. FEBS Lett. 545, 86–95 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

