Influencing Factors of Social Anxiety of Undergraduate Nursing Students Based on Random Forest Model: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39794003
- PMCID: PMC11723782
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.70137
Influencing Factors of Social Anxiety of Undergraduate Nursing Students Based on Random Forest Model: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Aim: Social anxiety is common among students, yet research specifically on undergraduate nursing students is scarce. Previous studies have identified various influencing factors but lack a clear ranking of their importance, making it challenging to implement effective intervention strategies with limited resources. This study aims to assess the level of social anxiety in undergraduate nursing students and rank the importance of its influencing factors, providing essential insights for developing efficient and targeted interventions.
Design: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 546 undergraduate nursing students in China.
Methods: Data were collected via a web-based questionnaire, which included the fear of positive and negative evaluation scale, the self-efficacy scale, and the social anxiety scale. The random forest model was employed to analyse the data and rank the importance of the influencing factors.
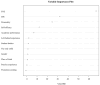
Results: The total social anxiety score among undergraduate nursing students was 11.20 ± 4.71. Social anxiety had a positive correlation with both fear of positive evaluation (r = 0.521, p < 0.001) and fear of negative evaluation (r = 0.648, p < 0.001) and a negative correlation with self-efficacy (r = -0.273, p < 0.001). According to the random forest model, the top five predictors of social anxiety in this study were fear of negative evaluation, fear of positive evaluation, personality traits, self-efficacy, and academic performance.
Conclusion: Attention to social anxiety in undergraduate nursing students is necessary, particularly for those with a higher fear of evaluations, introverted personalities, lower self-efficacy, and poor academic performance. Nursing educators should consider recognising social anxiety and developing personalised interventions tailored to the specific characteristics of these students.
Patient or public contribution: All participants contributed to the conducting of this study by completing self-reported questionnaires.
Keywords: influencing factors; random forest model; social anxiety; undergraduate nursing students.
© 2025 The Author(s). Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fear of negative evaluation: A cross-sectional study among undergraduate nursing students.Nurse Educ Today. 2023 Feb;121:105678. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105678. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Nurse Educ Today. 2023. PMID: 36527756
-
Latent profiles of academic resilience in undergraduate nursing students and their association with resilience and self-efficacy.Nurse Educ Pract. 2024 May;77:103949. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2024.103949. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Nurse Educ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38593563
-
Nurse academics and the teaching of undergraduate nursing numeracy: A cross-sectional study of self-reported confidence and anxiety.Nurse Educ Today. 2025 Jan;144:106422. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2024.106422. Epub 2024 Sep 22. Nurse Educ Today. 2025. PMID: 39321592
-
Fear of positive evaluation and social anxiety: A systematic review of trait-based findings.J Affect Disord. 2020 Mar 15;265:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.042. Epub 2020 Jan 13. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32090737
-
Self-Efficacy in a Nursing Context.2021 Mar 12. In: Haugan G, Eriksson M, editors. Health Promotion in Health Care – Vital Theories and Research [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2021. Chapter 12. 2021 Mar 12. In: Haugan G, Eriksson M, editors. Health Promotion in Health Care – Vital Theories and Research [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2021. Chapter 12. PMID: 36315720 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Annoni, A. M. , Petrocchi S., Camerini A. L., and Marciano L.. 2021. “The Relationship Between Social Anxiety, Smartphone Use, Dispositional Trust, and Problematic Smartphone Use: A Moderated Mediation Model.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2452. 10.3390/ijerph18052452. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao, C. X. , and Qi S. S.. 2021. “The Relationship Between Potential Categories of Emotion Regulation Self‐Efficacy and Social Anxiety in College Students.” Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medicine and Brain Science 30, no. 11: 1040–1044. 10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20210712-00393. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical