Girolline is a sequence context-selective modulator of eIF5A activity
- PMID: 39794322
- PMCID: PMC11724050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54838-2
Girolline is a sequence context-selective modulator of eIF5A activity
Abstract
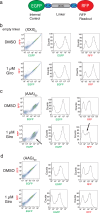
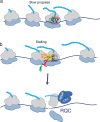
Natural products have a long history of providing probes into protein biosynthesis, with many of these compounds serving as therapeutics. The marine natural product girolline has been described as an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Its precise mechanism of action, however, has remained unknown. The data we present here suggests that girolline is a sequence-selective modulator of translation factor eIF5A. Girolline interferes with ribosome-eIF5A interaction and induces ribosome stalling where translational progress is impeded, including on AAA-encoded lysine. Our data furthermore indicate that eIF5A plays a physiological role in ribosome-associated quality control and in maintaining the efficiency of translational progress. Girolline helped to deepen our understanding of the interplay between protein production and quality control in a physiological setting and offers a potent chemical tool to selectively modulate gene expression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Chiaroni, A. et al. Crystal-structure and absolute-configuration of girolline. Health Eviron. Res. Online312, 49–53 (1991).
-
- Ahond, A. et al. Girolline, a new antitumoral compound extracted from the sponge, pseudaxinyssa-cantharella N-Sp (Axinellidae). Cr Acad. Sci. Ii307, 145–148 (1988).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

