Association between lymphocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in US adults: results from NHANES 2007-2018
- PMID: 39794792
- PMCID: PMC11721163
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02411-7
Association between lymphocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in US adults: results from NHANES 2007-2018
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) and metabolic syndrome (MetS) are significant global health challenges that increase the risk of various chronic diseases. The lymphocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (LHR) has emerged as a novel inflammatory metabolic marker. The present study focused on evaluating the association between the LHR and both IR and MetS.
Methods: We analyzed data from 14,779 adults aged ≥ 20 years from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2018). To investigate the relationship between LHR and both IR and MetS, we conducted multivariable logistic regression analyses. The reliability of the results was validated through both stratified and sensitivity analyses. Furthermore, we thoroughly examined possible nonlinear associations by implementing a restricted cubic spline in conjunction with a threshold effect analysis.
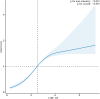
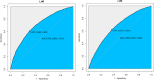
Results: Compared to the lowest LHR quartile, individuals in the highest quartile indicated significantly increased prevalence of IR (odds ratio = 3.72, 95% confidence intervals: 3.01-4.59) and MetS (odds ratio = 11.38, 95% confidence intervals: 8.85-14.63) in fully adjusted models. Subgroup analyses demonstrated that the association between the LHR and IR remained consistent across all subgroups, with no significant interaction effect observed. However, the association between LHR and MetS was more pronounced in female participants. Restricted cubic spline analyses revealed nonlinear associations between LHR and both IR and MetS. The threshold effect analyses identified inflection points at 0.055 for these non-linear relationships.
Conclusions: An elevated LHR was positively associated with the prevalence of IR and MetS, indicating its promising role in early screening and disease prevention through biological monitoring.
Keywords: Insulin resistance; Lymphocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; Metabolic syndrome; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The NHANES protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics, and all participants provided informed consent. As a secondary analysis of publicly available de-identified data, the present study did not require additional ethical review. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5. - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005;365:1415–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

