Efficacy of caerulomycin A in modulating macrophage polarization and cytokine response in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis
- PMID: 39794821
- PMCID: PMC11724434
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-02265-w
Efficacy of caerulomycin A in modulating macrophage polarization and cytokine response in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is characterized by an excessive immune response. Modulation of the immune response, particularly macrophage polarization, may provide therapeutic benefit. The effects of Caerulomycin A (caeA), a known STAT1 phosphorylation inhibitor, on macrophage polarization and inflammatory markers were explored using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis mouse model.
Methods: A sepsis model was established in C57BL/6 mice induced by intraperitoneal injection of LPS, and the survival rate of mice was observed after treatment with different doses of caeA to determine the optimal therapeutic dose. For in-vitro assays using the RAW264.7 macrophage cell line, the concentration of caeA that was non-toxic to cell survival was screened using the MTT assay, followed by the analyses by qRT-PCR, ELISA, Western blot and flow cytometry for M1/M2 type macrophage markers (CD86, NOS2, CD206, ARG1) and inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-10) expression. In addition, the phosphorylation levels of STAT1 and STAT6 in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway were detected.
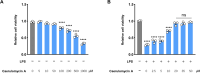
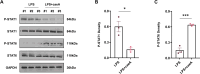
Results: The results of in-vivo experiments showed that caeA treatment (20 mg/kg) significantly increased the survival of LPS-induced septic mice and decreased the expression of M1-type macrophage markers (CD86 and NOS2) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) while increasing the expression of M2-type markers (CD206 and ARG1) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10) expression. In in-vitro experiments, 20 μM caeA effectively inhibited LPS-induced polarization of M1-type macrophages without affecting the activity of RAW264.7 cells, and caeA significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT1 yet enhanced the phosphorylation level of STAT6, as detected by Western blot.
Conclusions: CaeA effectively modulates macrophage polarization and attenuates the inflammatory response in septic mice, possibly by affecting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. These findings support further exploration of the potential of caeA as a therapeutic agent for sepsis.
Keywords: Caerulomycin A; Cytokine modulation; Immunomodulation; Macrophage polarization; Sepsis therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Animal-involved experiments were approved by the Animal Experimental Ethical Committee of Jinhua Central Hospital (Approval number: (Research) 2022-Ethics Review-44), adhering strictly to the guidelines for humane care outlined by the National Institutes of Health. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Oczkowski S, Alshamsi F, Belley-Cote E, Centofanti JE, Hylander Moller M, Nunnaly ME, Guidelines SSC, et al. highlights for the practicing clinician. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021;2022:132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

