Recent Progress in Polyolefin Plastic: Polyethylene and Polypropylene Transformation and Depolymerization Techniques
- PMID: 39795145
- PMCID: PMC11721993
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30010087
Recent Progress in Polyolefin Plastic: Polyethylene and Polypropylene Transformation and Depolymerization Techniques
Abstract
This paper highlights the complexity and urgency of addressing plastic pollution, drawing attention to the environmental challenges posed by improperly discarded plastics. Petroleum-based plastic polymers, with their remarkable range of physical properties, have revolutionized industries worldwide. Their versatility-from flexible to rigid and hydrophilic to hydrophobic-has fueled an ever-growing demand. However, their versatility has also contributed to a massive global waste problem as plastics pervade virtually every ecosystem, from the depths of oceans to the most remote terrestrial landscapes. Plastic pollution manifests not just as visible waste-such as fishing nets, bottles, and garbage bags-but also as microplastics, infiltrating food chains and freshwater sources. This crisis is exacerbated by the unsustainable linear model of plastic production and consumption, which prioritizes convenience over long-term environmental health. The mismanagement of plastic waste not only pollutes ecosystems but also releases greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide during degradation and incineration, thereby complicating efforts to achieve global climate and sustainability goals. Given that mechanical recycling only addresses a fraction of macroplastics, innovative approaches are needed to improve this process. Methods like pyrolysis and hydrogenolysis offer promising solutions by enabling the chemical transformation and depolymerization of plastics into reusable materials or valuable chemical feedstocks. These advanced recycling methods can support a circular economy by reducing waste and creating high-value products. In this article, the focus on pyrolysis and hydrogenolysis underscores the need to move beyond traditional recycling. These methods exemplify the potential for science and technology to mitigate plastic pollution while aligning with sustainability objectives. Recent advances in the pyrolysis and hydrogenolysis of polyolefins focus on their potential for advanced recycling, breaking down plastics at a molecular level to create feedstocks for new products or fuels. Pyrolysis produces pyrolysis oil and syngas, with applications in renewable energy and chemicals. However, some challenges of this process include scalability, feedstock variety, and standardization, as well as environmental concerns about emissions. Companies like Shell and ExxonMobil are investing heavily to overcome these barriers and improve recycling efficiencies. By leveraging these transformative strategies, we can reimagine the lifecycle of plastics and address one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. This review updates the knowledge of the fields of pyrolysis and hydrogenolysis of plastics derived from polyolefins based on the most recent works available in the literature, highlighting the techniques used, the types of products obtained, and the highest yields.
Keywords: hydrogenolysis; microplastics; polymers; pyrolysis; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




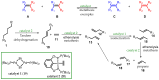


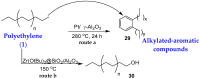

Similar articles
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polydiketoenamines for a Circular Plastics Economy.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Oct 4;55(19):2753-2765. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00308. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 36108255
-
Plastic pollution and potential solutions.Sci Prog. 2018 Sep 1;101(3):207-260. doi: 10.3184/003685018X15294876706211. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Sci Prog. 2018. PMID: 30025551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disposal of plastic mulching film through CO2-assisted catalytic pyrolysis as a strategic means for microplastic mitigation.J Hazard Mater. 2022 May 15;430:128454. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128454. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 35168100
-
Life cycle environmental impacts of chemical recycling via pyrolysis of mixed plastic waste in comparison with mechanical recycling and energy recovery.Sci Total Environ. 2021 May 15;769:144483. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144483. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33486181
Cited by
-
Pyrolysis of Polypropylene and Nitrile PPE Waste: Insights into Oil Composition, Kinetics, and Steam Cracker Integration.Molecules. 2025 Aug 12;30(16):3351. doi: 10.3390/molecules30163351. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40871506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambaye T.G., Djellabi R., Vaccari M., Prasad S., Aminabhavi T.M., Rtimi S. Emerging technologies and sustainable strategies for municipal solid waste valorization: Challenges of circular economy implementtion. J. Clean. Prod. 2023;423:138708. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138708. - DOI
-
- Gomollón-Bel F. IUPAC Top Ten Emerging Technologies in Chemistry 2021. Chem. Int. 2021;43:13–20. doi: 10.1515/ci-2021-0404. - DOI
-
- IUPAC Announces the 2023 Top Ten Emerging Technologies in Chemistry. [(accessed on 12 September 2024)]. Available online: https://iupac.org/iupac-2023-top-ten/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

