CDC20 and CCNB1 Overexpression as Prognostic Markers in Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 39795587
- PMCID: PMC11719780
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15010059
CDC20 and CCNB1 Overexpression as Prognostic Markers in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
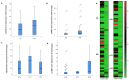
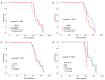
Background: Bladder cancer (BC) is one of the ten most common cancers worldwide, with a high recurrence rate and significant variation in clinical outcomes based on tumor grade and stage. This study aimed to investigate the gene expression profiles at different cancer stages to assess their potential prognostic value. Methods: RNA was extracted from paraffin-embedded BC tissues and the gene expression levels of CDC20 and CCNB1 were analyzed using qRT-PCR. A total of 54 BC patient samples were included in the analysis and categorized into low-grade (LG) (n = 23) and high-grade (HG) (n = 31) tumors, as well as stages pTa, pT1, and pT2. Results: CDC20 gene expression was significantly higher in the HG group (mean fold-change: 16.1) compared to the LG group (mean fold-change: 10.54), indicating a significant association with tumor grade (p = 0.039). However, no significant differences were observed in CDC20 expression across the cancer stages. For CCNB1, while gene expression was significantly elevated in higher-stage tumors (pT2 vs. pTa; p = 0.038), no significant association was found between CCNB1 expression and tumor grade. Survival analysis revealed that increased CCNB1 expression and advanced cancer stage were associated with poorer overall survival, whereas no significant impact of CDC20 expression or tumor grade on survival was observed. Correlation analysis indicated a positive relationship between CDC20 expression and tumor grade (r = 0.284, p = 0.038) and between CCNB1 expression and tumor stage (r = 0.301, p = 0.027). Conclusions: Our findings suggest that CDC20 overexpression is linked to higher tumor grades, while CCNB1 overexpression is associated with more advanced cancer stages in BC. These results underscore the potential utility of CDC20 and CCNB1 as biomarkers for tumor prognosis and as therapeutic targets. Further studies with larger cohorts are needed to validate these findings and better understand the molecular mechanisms driving BC progression.
Keywords: CDC20; Cyclin B1; bladder cancer; cancer stage; overall survival; tumor grade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of BUB1B, CCNB1, CDC7, CDC20, and MCM3 in Tumor Tissues Predicted Worse Overall Survival and Disease-Free Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 30;2018:7897346. doi: 10.1155/2018/7897346. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30363964 Free PMC article.
-
The intercorrelation among CCT6A, CDC20, CCNB1, and PLK1 expressions and their clinical value in papillary thyroid carcinoma prognostication.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24609. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24609. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35838025 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance of cyclin B1 (CCNB1) in invasive breast cancer with emphasis on its contribution to lymphovascular invasion development.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Apr;198(3):423-435. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06801-2. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36418517 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatical Analysis of Gene Expression Omnibus Database Associates TAF7/CCNB1, TAF7/CCNA2, and GTF2E2/CDC20 Pathways with Glioblastoma Development and Prognosis.World Neurosurg. 2020 Jun;138:e492-e514. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.02.159. Epub 2020 Mar 5. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32147549
-
Prognostic significance of CDC20 expression in malignancy patients: A meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 21;12:1017864. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1017864. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36479068 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Repurposing ProTAME for Bladder Cancer: A Combined Therapeutic Approach Targeting Cell Migration and MMP Regulation.Biology (Basel). 2025 Mar 5;14(3):263. doi: 10.3390/biology14030263. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han S.H., Yuk H.D. Epidemiology of Urologic Cancer in Korea: Nationwide Trends in the Last 2 Decades. J. Urol. Oncol. 2023;21:32–44. doi: 10.22465/juo.234600080004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

