SgR1, Encoding a Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing Receptor-like Protein, Is a Major Aphid (Schizaphis graminum) Resistance Gene in Sorghum
- PMID: 39795877
- PMCID: PMC11719657
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26010019
SgR1, Encoding a Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing Receptor-like Protein, Is a Major Aphid (Schizaphis graminum) Resistance Gene in Sorghum
Abstract
Greenbug, Schizaphis graminum, is one of the important cereal aphid pests of sorghum in the United States and other parts of the world. Sorghum bicolor variety PI 607900 carries the Schizaphis graminum resistance (SgR1) gene that underlies plant resistance to greenbug biotype I (GBI). Now, the SgR1 has been determined as the major gene conferring greenbug resistance based on the strong association of its presence with the resistance phenotype in sorghum. In this study, we have successfully isolated the SgR1 gene using a map-based cloning approach, and subsequent molecular characterization revealed it encodes a leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like protein (LRR-RLP). According to DNA sequence analysis, the SgR1 gene are conserved among GBI-resistance sorghum accessions but are variable within susceptible lines. Furthermore, an InDel (-965 nt) at its promoter region and a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP, 592 nt) in the CDS of the SgR1 were detected and they are well conserved within resistant genotypes. When the SgR1 gene was cloned and transferred into Arabidopsis plants, the SgR1 was activated in the transgenic Arabidopsis plants in response to attack by green peach aphids according to the results of the histochemical assay, and GUS activity was detected in situ in spots around the vasculature of the leaf where the phloem is located, suggesting its biological function in those transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Overall, this study confirms that the SgR1 gene coding for an LRR-RLP is the major resistance gene to greenbug, a destructive pest in sorghum and wheat. This represents the first greenbug resistance gene cloned so far and indicates that the simple-inherited GBI resistance gene can be used for sorghum improvement with genetic resistance to GBI via molecular breeding or cross-based conventional breeding technologies.
Keywords: LRR-RLP; aphid; gene cloning; host plant resistance; insect resistance; sorghum.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
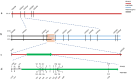

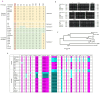

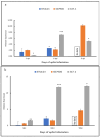

References
-
- Harvey T.L., Hackerott H.L. Recognition of a Greenbug Biotype Injurious to Sorghum1. J. Econ. Entomol. 1969;62:776–779. doi: 10.1093/jee/62.4.776. - DOI
-
- Harvey T.L., Kofoid K.D., Martin T.J., Sloderbeck P.E. A New Greenbug Virulent to E-Biotype Resistant Sorghum. Crop Sci. 1991;31:1689–1691. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1991.0011183X003100060062x. - DOI
-
- Harvey T.L., Wilde G.E., Kofoid K.D., Bramel-Cox P.J. Temperature Effects on Resistance to Greenbug (Homoptera: Aphididae) Biotype I in Sorghum. J. Econ. Entomol. 1994;87:500–503. doi: 10.1093/jee/87.2.500. - DOI
-
- Eddleman B.R., Chang C.C., McCarl B.A. Economic Benefits from Grain Sorghum Variety Improvement in the United States. In: Wiseman B.R., Webster J.A., editors. Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits of Resistance in Field Crops. Entomological Society of America; Annapolis, ML, USA: 1999. pp. 17–44. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

