A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Decreases the Severity of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 39795896
- PMCID: PMC11720533
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26010032
A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Decreases the Severity of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
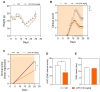
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease, with inflammation and oxidative stress in the central nervous system being the main triggers. There are many drugs that reduce the clinical signs of MS, but none of them cure the disease. Food proteins have been shown to contain encrypted peptides that can be released after hydrolysis and exert numerous biological activities. Recently, we have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of a lupin protein hydrolysate (LPH) both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate whether LPH is capable of reducing the clinical signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model of MS. EAE was induced in female C57BL/6N mice and they were treated intragastrically with LPH (100 mg/kg) or vehicle (control group) from day 0 (prophylactic approach) or from the onset of the disease (day 12 post-induction; therapeutic approach) and the clinical score of each mouse was recorded daily. Prophylactic treatment with LPH reduced the clinical score of the mice compared to the control group, as well as the maximum and cumulative scores, without changing the day of onset of the symptoms while the therapeutic intervention did not significantly improve the severity of the disease. For the first time, we demonstrated that prophylactic administration of LPH reduces the severity of MS, suggesting a potential nutraceutical or new functional foods in neuroinflammation. However, further studies are needed to confirm this nutritional effect in a clinical context.
Keywords: EAE; MS; functional foods; hydrolysates; neurodegeneration; vegetable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bioactive Peptides from Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Prevent the Early Stages of Atherosclerosis in Western Diet-Fed ApoE-/- Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Jul 13;70(27):8243-8253. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00809. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35767743 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine treatment enhances regulatory T cells and reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 14;8(6):e65913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065913. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23799062 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bioavailable Protein Hydrolysates from Lupin-Derived Agri-Waste.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 4;11(10):1458. doi: 10.3390/biom11101458. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680091 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin synergistically potentiates the effect of methylprednisolone on reducing neuroinflammation in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse model of multiple sclerosis.J Autoimmun. 2024 Sep;148:103298. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2024.103298. Epub 2024 Jul 26. J Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 39067314
-
Effects of coenzyme Q10 on the ratio of TH1/TH2 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of multiple sclerosis in C57BL/6.Iran Biomed J. 2014;18(4):203-11. doi: 10.6091/ibj.13362.2014. Iran Biomed J. 2014. PMID: 25326018 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

