NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
- PMID: 39796162
- PMCID: PMC11720452
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26010306
NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Abstract
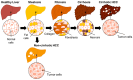
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), recently renamed metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is the most prevalent liver disease worldwide. It is associated with an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the background of cirrhosis or without cirrhosis. The prevalence of NAFLD-related HCC is increasing all over the globe, and HCC surveillance in NAFLD cases is not that common. In the present review, we attempt to summarize promising treatments and clinical trials focused on NAFLD, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and HCC in the past five to seven years. We categorized the trials based on the type of intervention. Most of the trials are still running, with only a few completed and with conclusive results. In clinical trial NCT03942822, 25 mg/day of milled chia seeds improved NAFLD condition. Completed trial NCT03524365 concluded that Rouxen-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or sleeve gastrectomy (SG) results in histological resolution of NASH without worsening of fibrosis, while NCT04677101 validated sensitivity/accuracy of blood biomarkers in predicting NASH and fibrosis stage. Moreover, trials with empagliflozin (NCT05694923), curcuvail (NCT06256926), and obeticholic acid (NCT03439254) were completed but did not provide conclusive results. However, trial NCT03900429 reported effective improvement in fibrosis by at least one stage, without worsening of NAFLD activity score (NAS), as well as improvement in lipid profile of the NASH patients by 80 or 100 mg MGL-3196 (resmetirom). Funded by Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Rezdiffra (resmetirom), used in the clinical trial NCT03900429, is the first FDA-approved drug for the treatment of NAFLD/NASH.
Keywords: cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic HCC; clinical trials; hepatocellular carcinoma; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and therapeutic targets.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 8;14:1148934. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1148934. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37361533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Setting of Non-cirrhotic Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Metabolic Syndrome: US Experience.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Oct;60(10):3142-8. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3821-7. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26250831
-
The characteristics and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease without cirrhosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 May;35(5):862-869. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14867. Epub 2019 Dec 3. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31597206
-
Utilization of animal models to investigate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42762-42776. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8641. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27072576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NAFLD-Related Hepatocarcinoma: The Malignant Side of Metabolic Syndrome.Cells. 2021 Aug 9;10(8):2034. doi: 10.3390/cells10082034. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to overcome immune checkpoint inhibitor resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 5;44(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03490-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40764998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between PLT, MPV, PDW and liver fibrosis and inflammatory activity in patients with NAFLD: A retrospective case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 15;104(33):e43815. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043815. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40826707 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 27;47(3):154. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030154. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cultural and Molecular Factors Predisposed to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2025 May 26;17(11):1797. doi: 10.3390/nu17111797. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends and visualization analysis of research on MASLD-Related hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 11;16(1):1057. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02858-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40500549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karlsen T.H., Sheron N., Zelber-Sagi S., Carrieri P., Dusheiko G., Bugianesi E., Pryke R., Hutchinson S.J., Sangro B., Martin N.K., et al. The EASL-Lancet Liver Commission: Protecting the next generation of Europeans against liver disease complications and premature mortality. Lancet. 2022;399:61–116. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01701-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

