EML4-ALK: Update on ALK Inhibitors
- PMID: 39796163
- PMCID: PMC11719670
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26010308
EML4-ALK: Update on ALK Inhibitors
Abstract
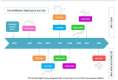
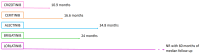
Since the discovery of the first-generation ALK inhibitor, many other tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been demonstrated to be effective in the first line or further lines of treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EMLA4-ALK translocation. This review traces the main milestones in the treatment of ALK-positive metastatic patients and the survival outcomes in the first-line and second-line settings with different ALK inhibitors. It presents the two options available for first-line treatment at the present time: sequencing different ALK inhibitors versus using the most potent inhibitor in front-line treatment. The efficacy outcomes of different ALK inhibitors in the first-line setting; the molecular profile of the disease, including mutation resistances and ALK variants and co-mutations; and patients' co-morbidities and inhibitor toxicities should be taken into account to address the choice of the first-line treatment, as suggested in this review.
Keywords: EMLA4-ALK; NSCLC; TKI; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shaw A.T., Yeap B.Y., Mino-Kenudson M., Digumarthy S.R., Costa D.B., Heist R.S., Solomon B., Stubbs H., Admane S., McDermott U., et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:4247–4253. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.6993. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical