The Impact of Social Media on Disordered Eating: Insights from Israel
- PMID: 39796614
- PMCID: PMC11722979
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17010180
The Impact of Social Media on Disordered Eating: Insights from Israel
Abstract
Background: Social media platforms have become integral to daily life and increasingly disseminate health, nutrition, and food information. While these platforms can offer evidence-based nutrition education and meal planning guidance, a significant portion of content promotes unrealistic beauty standards and unhealthy weight-loss practices, potentially contributing to disordered eating behaviors. The increasing prevalence of disordered eating, characterized by abnormal eating behaviors and attitudes, has become a global public health concern. This study examines whether social media consumption correlates with disordered eating symptoms in Israeli college students.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among college students at Ashkelon Academic College in Israel. The questionnaire assessed demographics, social media usage (platforms used, frequency, and content followed), body satisfaction, and disordered eating symptoms, measured via the Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).
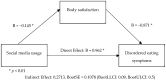
Results: The study sample comprised 580 students (73% were female and 27% were male) with a mean age of 27.87 years. Participants predominantly used multiple social media platforms, with a majority following food-, eating-, and health-related content. Despite having a normal BMI, a substantial number of participants reported body dissatisfaction. The results indicated a positive correlation between social media use and disordered eating symptoms. Individuals who frequently engaged with food-related content on social media exhibited higher levels of disordered eating. Moreover, body satisfaction emerged as a significant mediator in the relationship between social media use and disordered eating symptoms.
Conclusions: The findings of this study support the growing body of evidence linking social media use to disordered eating behaviors among young adults. Developing targeted interventions that promote media literacy and foster body positivity is essential. Additionally, future research should explore the long-term effects of social media on eating behaviors and the effectiveness of different prevention strategies.
Keywords: BMI; Facebook; Instagram; college students; diet; disordered eating; eating disorders; eating habits; influencers; nutrition; social media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social Media, Thin-Ideal, Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Attitudes: An Exploratory Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Oct 29;16(21):4177. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214177. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31671857 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Social Media on Eating Disorder Risk and Self-Esteem Among Adolescents and Young Adults: A Psychosocial Analysis in Individuals Aged 16-25.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 8;17(2):219. doi: 10.3390/nu17020219. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861349 Free PMC article.
-
Disordered eating attitudes among Iranian university students of medical sciences: The role of body image perception.Nutr Health. 2020 Jun;26(2):127-133. doi: 10.1177/0260106020912657. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Nutr Health. 2020. PMID: 32233905
-
A Review of Food-Related Social Media and Its Relationship to Body Image and Disordered Eating.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 18;17(2):342. doi: 10.3390/nu17020342. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Multifactorial Determinants of Childhood Eating Behaviors: Insights and Interventions Using the Social Ecological Model.Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;12(3):388. doi: 10.3390/children12030388. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Screen to Plate: How Instagram Cooking Videos Promote Healthy Eating Behaviours in Established Adulthood.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1133. doi: 10.3390/nu17071133. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218891 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent Nutritional Patterns and Health Behaviors in Romania: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 25;17(9):1448. doi: 10.3390/nu17091448. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362757 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Mediterranean Diet, Processed Food Consumption, and Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression: Cross-Sectional Study Among Israeli Adults.Foods. 2025 Apr 24;14(9):1485. doi: 10.3390/foods14091485. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361567 Free PMC article.
-
Food, Quality of Life and Mental Health: A Cross-Sectional Study with Federal Education Workers.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 31;17(15):2519. doi: 10.3390/nu17152519. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akram W., Kumar R. A study on positive and negative effects of social media on society. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017;5:351–354. doi: 10.26438/ijcse/v5i10.351354. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical