miRNAs Dysregulated in Human Papillomavirus-Associated Benign Prostatic Lesions and Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 39796656
- PMCID: PMC11718816
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17010026
miRNAs Dysregulated in Human Papillomavirus-Associated Benign Prostatic Lesions and Prostate Cancer
Abstract
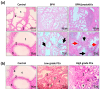
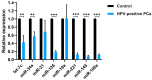
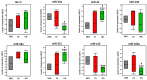
Prostate pathologies, including chronic prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostate cancer (PCa), are strongly associated with chronic inflammation, which is a key risk factor and hallmark of these diseases [...].
Keywords: BPH; HPV; angiogenesis; apoptosis; functional enrichment analysis; inflammation; interactomic analysis; metastasis; miRNAs; proliferation; prostate cancer; prostatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress parameters in patients with prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis: A prospective controlled study.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Oct;26(7):1095-1099. doi: 10.17219/acem/66837. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29211357
-
The controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: the role of inflammation.Eur Urol. 2011 Jul;60(1):106-17. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.03.055. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Eur Urol. 2011. PMID: 21497433 Review.
-
Prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostate cancer: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study and clinical implications for these patients' populations.Biol Direct. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00575-x. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 39695756 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and/or Prostatitis on the Risk of Prostate Cancer in Korean Patients.World J Mens Health. 2021 Apr;39(2):358-365. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.190135. Epub 2020 Feb 5. World J Mens Health. 2021. PMID: 32202082 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Basis and Clinical Consequences of Chronic Inflammation in Prostatic Diseases: Prostatitis, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, and Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;15(12):3110. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123110. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Avenues for the Detection of Cancer-Associated Viral Genome Integrations Using Long-Read Sequencing Technologies.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 22;17(11):1740. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111740. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols from Bacopa procumbens Nanostructured with Gold Nanoparticles Stimulate Hair Growth Through Apoptosis Modulation in C57BL/6 Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 9;17(2):222. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020222. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oseni S.O., Naar C., Pavlović M., Asghar W., Hartmann J.X., Fields G.B., Esiobu N., Kumi-Diaka J. The Molecular Basis and Clinical Consequences of Chronic Inflammation in Prostatic Diseases: Prostatitis, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, and Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2023;15:3110. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shiau M.-Y., Fan L.-C., Yang S.-C., Tsao C.-H., Lee H., Cheng Y.-W., Lai L.-C., Chang Y.-H. Human Papillomavirus Up-Regulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression and Activity by Inducing Interleukin-8 in Lung Adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e54423. doi: 10.1371/annotation/a50fa759-93fb-444d-9523-9d4a805ef898. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

