Does the Performance of a Six-Minute Walking Test Predict Cardiopulmonary Complications After Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery Anatomic Lung Resection?
- PMID: 39796663
- PMCID: PMC11718962
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17010032
Does the Performance of a Six-Minute Walking Test Predict Cardiopulmonary Complications After Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery Anatomic Lung Resection?
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of the present study was to verify if performance in the 6-min walking test (6MWT) during the preoperative evaluation phase is associated with the development of cardiopulmonary postoperative complications in patients who underwent uniportal VATS (U-VATS) for lung cancer.
Methods: This retrospective, monocentric study included patients submitted to U-VATS anatomical lung resections (March 2022-December 2023). The patients were enrolled in a preoperative rehabilitation program carried out 15 days before surgery. The 6MWT was performed at counseling (T0) and after pre-habilitation (T1). Univariate analysis followed by logistic regression verified the association of baseline patients' characteristics and performance in the 6MWT (meters walked during T0 and T1 and the difference between T1 and T0-T1-T0 variation) with postoperative cardiopulmonary complications (CPCs). Youde's index was used to establish the optimal cut-offs for ergometric parameters significantly correlated with CPCs.
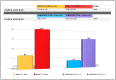
Results: We enrolled 212 patients scheduled to undergo U-VATS lung resection (lobectomies: 177; bilobectomies: 2; segmentectomies: 33). Twenty-three (10.8%) patients developed CPCs. None of the baseline patients' characteristics were associated with CPCs. Complicated patients showed more significant differences compared to non-complicated ones for meters walked during the 6MWT T1 (6MWT-T1-complicated: 450 vs. 6MWT-T1-non-complicated: 517; p: 0.01) and for variation-T1-T0 (variation-T1-T0-complicated: 4 m vs. variation-T1-T0-non-complicated: 20 m; p: 0.02). The best cut-offs for discriminating between patients with CPCs and those with uneventful courses were 458 m for 6MWT-T1 and 31 m for variation-T1-T0. After multivariate analysis, 6MWT-T1 < 458 m and variation-T1-T0 < 31 m were the unique parameters independently correlated with CPCs (p: 0.03 and p: 0.05, respectively).
Conclusions: The 6MWT results (in particular, 6MWT-T1 < 458 m and variation-T1-T0 < 31 m) in the context of a pre-habilitation program are associated with the development of CPCs after U-VATS lung resection.
Keywords: 6MWT; complications; lung resection; minimally invasive surgery; pre-habilitation; risk assessment; uniportal VATS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Howington J.A., Blum M.G., Chang A.C., Balekian A.A., Murthy S.C. Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e278S–e313S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2359. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brunelli A., Kim A.W., Berger K.I., Addrizzo-Harris D.J. Physiologic evaluation of the patient with lung cancer being considered for resectional surgery: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e166S–e190S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2395. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brunelli A., Charloux A., Bolliger C.T., Rocco G., Sculier J.P., Varela G., Licker M., Ferguson M.K., Faivre-Finn C., Huber R.M., et al. ERS/ESTS clinical guidelines on fitness for radical therapy in lung cancer patients (surgery and chemo-radiotherapy) Eur. Respir. J. 2009;34:17–41. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00184308. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

