Evaluation of Predictive Factors for Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization Success in Treating Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas
- PMID: 39796672
- PMCID: PMC11718885
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17010042
Evaluation of Predictive Factors for Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization Success in Treating Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas
Abstract
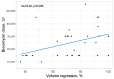
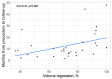
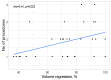
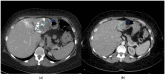
Introduction: Giant hepatic hemangiomas are challenging to manage, requiring effective therapeutic approaches. Transarterial bleomycin-lipiodol embolization (TACE) has shown promise as a treatment option, yet predictive factors for its success are not well defined. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of TACE for giant hepatic hemangiomas and identify factors influencing treatment outcomes. Methods: A retrospective analysis of 31 adult patients who underwent TACE with bleomycin and lipiodol between December 2014 and October 2022 was conducted. Clinical parameters including age, sex, hemangioma location, lesion size, bleomycin dose, number of TACE sessions, and follow-up duration were evaluated. The primary outcome was hemangioma volume reduction, with statistical analyses identifying factors associated with significant lesion regression. Results: Higher bleomycin doses and longer intervals from procedure to follow-up were positively correlated with hemangioma volume reduction, while variables such as patient sex and lesion location showed no statistically significant impact on clinical success. The findings suggest that increased bleomycin dosage and extended follow-up periods may enhance treatment efficacy. Conclusions: The study identifies bleomycin dose and follow-up duration as predictive factors for TACE success in treating giant hepatic hemangiomas, underscoring their role in optimizing therapeutic strategies. These insights contribute to improved treatment personalization for patients with giant hepatic hemangiomas and highlight the need for further prospective studies to validate and expand upon these findings.
Keywords: bleomycin; giant hepatic hemangiomas; lipiodol; predictive factors; transarterial bleomycin–lipiodol embolization; treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

