The IL-23R and Its Genetic Variants: A Hitherto Unforeseen Bridge Between the Immune System and Cancer Development
- PMID: 39796684
- PMCID: PMC11718844
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17010055
The IL-23R and Its Genetic Variants: A Hitherto Unforeseen Bridge Between the Immune System and Cancer Development
Abstract
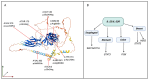
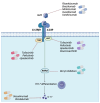
IL-23R (interleukin-23 receptor), found on the surface of several immune cells, plays a key role in the immune system. Indeed, this process is not limited to the inflammatory response but also plays a role in the adaptive immune response. The binding between IL-23R and its specific ligand, the interleukin 23, initiates a number of specific signals by modulating both properties and behavior of immune cells. In particular, it is critical for the regulation of T helper 17 cells (Th17). Th17s are a subset of T cells involved in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, as well as in cancer. The clinical relevance of IL-23R is underscored by its association with an elevated susceptibility or diminished vulnerability to a spectrum of diseases, including psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Evidence has emerged that suggests it may also serve to predict both tumor progression and therapeutic responsiveness. It is noteworthy that the IL-23/IL-23R pathway is emerging as a promising therapeutic target. A number of biologic drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies, are currently developing with the aim of blocking this interaction, thus reducing inflammation. This represents a significant advancement in the field of medicine, offering new hope for pursuing more effective and personalized treatments. Recent studies have also investigated the role of such a pathway in autoimmune diseases, and its potential impact on infections as well as in carcinogenesis. The aim of this review is to focus on the role of IL-23R in immune genetics and its potential for modulating the natural history of neoplastic disease.
Keywords: IL-23R; Th17; genetic variants; immune cells; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Parham C., Chirica M., Timans J., Vaisberg E., Travis M., Cheung J., Pflanz S., Zhang R., Singh K.P., Vega F., et al. A Receptor for the Heterodimeric Cytokine IL-23 Is Composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a Novel Cytokine Receptor Subunit, IL-23R. J. Immunol. 2002;168:5699–5708. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5699. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

