Improving Molecular Design with Direct Inverse Analysis of QSAR/QSPR Model
- PMID: 39797757
- PMCID: PMC11724648
- DOI: 10.1002/minf.202400227
Improving Molecular Design with Direct Inverse Analysis of QSAR/QSPR Model
Abstract
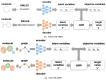
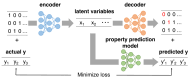
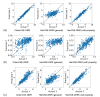
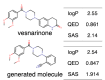
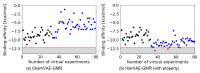
Recent advances in machine learning have significantly impacted molecular design, notably the molecular generation method combining the chemical variational autoencoder (VAE) with Gaussian mixture regression (GMR). In this method, a mathematical model is constructed with X as the latent variable of the molecule and Y as the target properties and activities. Through direct inverse analysis of this model, it is possible to generate molecules with the desired target properties. However, this approach outputs many strings that do not follow the simplified molecular input line entry system grammar and generates unrealistic chemical structures in which the properties and activity do not satisfy the target values. In this study, we focus on hierarchical VAE using molecular graphs to address these issues. We confirm that the combination of hierarchical VAE and GMR does not generate invalid outputs and returns molecules that simultaneously satisfy multiple target values. Moreover, we use this method to identify several molecules that are predicted to exhibit activity against drug targets.
Keywords: autoencoder; cheminformatics; drug design; machine learning; virtual screening.
© 2025 The Author(s). Molecular Informatics published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- C. Bilodeau, W. Jin, T. Jaakkola, R. Barzilay, K. F. Jensen, “Generative models for molecular discovery: Recent advances and challenges”, Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science 12 (2022): e1608.
-
- Weininger D., “SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules”, Journal of Chemical Infornation Computer Sciences 28 (1988): 31–36, 10.1021/ci00057a005. - DOI
-
- Krenn M., Hase F., Nigam A., Friederich P., Aspuru-Guzik A., “Self-referencing embedded strings (SELFIES): A 100% robust molecular string representation”, Machine Learning Science and Technology 1 (2020): 045024, 10.1088/2632--2153/aba947. - DOI
-
- D. P. Kingma, M. Welling, “Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes ”, Cornell University Library 2018, arXiv:1312.6114.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

