The Last Decade in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Advances in Understanding Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Quantification, Prognosis, Treatment Strategies, and Monitoring Response
- PMID: 39797879
- PMCID: PMC12273739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2024.10.011
The Last Decade in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Advances in Understanding Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Quantification, Prognosis, Treatment Strategies, and Monitoring Response
Abstract
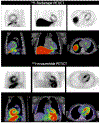
Cardiac amyloidosis represents a unique disease process characterized by amyloid fibril deposition within the myocardial extracellular space. Advances in multimodality cardiac imaging enable accurate diagnosis and facilitate prompt initiation of disease-modifying therapies. Furthermore, rapid advances in multimodality imaging have enriched understanding of the underlying pathogenesis, enhanced prognostication, and resulted in the development of imaging-based markers that reflect the amyloid burden, which is of increasing importance when assessing the response to treatment. Whereas conventional therapies have focused on reducing amyloid formation and subsequent stabilization of the cardiac disease process, novel agents are being developed to accelerate the immune-mediated removal of amyloid fibrils from the heart. In this context, the ability to track changes in the amyloid burden over time is of paramount importance. Although advanced imaging techniques have shown efficacy in tracking the treatment response, future research focused on improved precision through use of artificial intelligence may augment the detection of changes earlier in the course of treatment.
Keywords: Cardiac amyloidosis; systemic light-chain amyloidosis; transthyretin amyloidosis.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures Dr Fontana has received support from the British Heart Foundation Intermediate Clinical Research Fellowship (FS/18/21/33447) and has received consulting fees from Intellia, Novo-Nordisk, Pfizer, Eidos, Prothena, Akcea, Alnylam, Caleum, Alexion, Janssen, Ionis, and AstraZeneca. Dr Cuddy has received grants from National Institutes of Health award National Institutes of Health 1K23HL166686-01 and the American Heart Association award 23CDA857664; and has served on advisory boards for Bridge Bio, Ionis, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Novo Nordisk. Dr Singh has received grants from the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology/Pfizer and is on the speakers bureau for Pfizer and AstraZeneca. Dr Hanna has served on advisory boards for Alnylam, Bridge Bio, Pfizer, Ionis, and Alexion Pharmaceuticals. Dr Ruberg has received grants from National Institutes of Health awards R01HL139671 and R01AG081582; has received research grants to his institution from Akcea, Anumana, and Pfizer; and has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Attralus. Dr Grogan has received grants and/or consulting fees paid to her institution from Anumana, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Attralus, BridgeBio/Eidos, Pfizer, Janssen, and NovoNordisk. Dr Gilmore has received consulting fees from Ionis, Eidos, Intellia, Alnylam, and Pfizer.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

