Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: the Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management
- PMID: 39797961
- PMCID: PMC11724794
- DOI: 10.1007/s13679-024-00597-6
Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: the Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management
Abstract
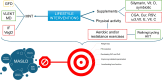
Purpose of review: This narrative review explores the role of Medical Nutritional Therapy (MNT) in managing Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), previously known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. It aims to examine the effectiveness of specific nutritional strategies in preventing and treating this obesity-linked liver disease.
Recent findings: Emerging evidence underscores the benefits of the Mediterranean diet, low-carbohydrate diets, and intermittent fasting in reducing liver fat, improving insulin sensitivity, and mitigating inflammation. Supplementing with vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, and silymarin can potentially reduce liver fibrosis and promote liver health. MNT is a key intervention for MASLD management, emphasizing dietary patterns, caloric restriction, and nutraceutical supplementation. Integrating these strategies with lifestyle modifications, including regular physical activity, offers a comprehensive approach to improving metabolic and liver outcomes in patients with MASLD. Further research is needed to refine and personalize these therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Liver fibrosis; Medical Nutritional Therapy (MNT); Mediterranean diet; Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD); Nutraceutical supplementation; Obesity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent: This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

