The mediating role of inflammatory biomarkers in the association between serum copper and sarcopenia
- PMID: 39799188
- PMCID: PMC11724950
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84011-0
The mediating role of inflammatory biomarkers in the association between serum copper and sarcopenia
Abstract
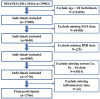
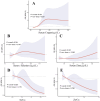
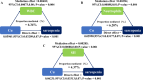
This study aims to investigate the association between serum copper (Cu), selenium (Se), zinc (Zn), Se/Cu and Zn/Cu ratios and the risk of sarcopenia. In this study, which involved 2766 adults aged ≥ 20 years enrolled in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2011 to 2016, multivariable logistic regression, restricted cubic spline (RCS) models and mediation analyses were used. After full adjustment, multivariable logistic regression revealed that higher serum copper levels were correlated with an increased risk of sarcopenia. Conversely, higher serum Se/Cu (OR 0.45, 95% CI 0.23-0.89, P = 0.023) and Zn/Cu (OR 0.49, 95% CI 0.27-0.90, P = 0.024) were associated with a decreased risk of sarcopenia. The RCS curve indicated a non-linear, roughly inverted L-shaped relationship between serum Cu and sarcopenia risk (P non-linear < 0.001). Additionally, Se/Cu (P non-linear = 0.179) and Zn/Cu (P non-linear = 0.786) showed negative linear associations with sarcopenia risk. Furthermore, white blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil count, and systemic inflammation index (SII) were identified as significant mediators in the relationship between serum Cu and the risk of sarcopenia, with mediation proportions of 6.34%, 6.20%, and 4.37%, respectively (all P < 0.05). Therefore, balancing essential trace metals is crucial for maintaining muscle health.
Keywords: Copper; NHANES; Sarcopenia; Selenium; Zinc.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Güngör, Ö., Güzel, F. B., Ulu, S. & Zadeh, K. K. Sarcopenia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Turk. J. Nephrol.31, 3–6 (2022). - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 823B2059/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024CX142/Graduate Innovation Program of Jilin University
- U21A20390/Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20230204075YY/Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program
- 20240305034YY/Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

