The antibacterial capabilities of alginate encapsulated lemon essential oil nanocapsules against multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 39799196
- PMCID: PMC11724895
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81948-0
The antibacterial capabilities of alginate encapsulated lemon essential oil nanocapsules against multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: The antibacterial capabilities of alginate encapsulated lemon essential oil nanocapsules against multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 11;15(1):8403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92797-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069255 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
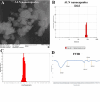
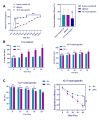
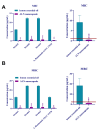
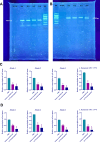
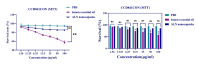
Controlling microbial pollutants is a significant public health concern as they cause several chronic microbial infections and illnesses. In recent years, essential oils (EOs) have become intriguing alternatives for synthetic antimicrobials due to their biodegradability, natural source extraction, and strong antibacterial properties. The bactericidal properties of alginate containing lemon essential oil were examined in this investigation. Following the screening of the MDR strains, the morphological properties of the produced nanoparticles were examined using SEM, DLS, and FTIR. Additionally, the durability, effectiveness, and drug dispersion of encapsulation were assessed. Bacterial virulence factor gene amounts were measured using Q-real-time PCR. Concurrently, the cytotoxic effect of the nanomaterials was evaluated using MTT techniques. Nanoparticles of lemon essential oil encapsulated in alginate, measuring 500 ± 19.32 nm in size, with entrapment efficiency of 77.73 ± 1.78% and were stable for 60 days at 4 °C. Alginate encapsulated with lemon essential oil nanoparticles (ALN) exhibited potent antibacterial qualities, according to the biological investigation. Their ability to decrease the transcription of bacterial virulence genes at least statistically significantly (P ≤ 0.05) served as evidence for this. Between 1.56 and 100 µg/mL (P ≤ 0.01), ALN exhibited lower cytotoxicity against CCD841CoN than free lemon essential oil. The findings show that ALN nanoparticles have the potential to be a breakthrough in the fight against highly resistant illnesses. ALN nanoparticles' potent antibacterial efficacy against MDR strains of Acinetobacter baumannii may inspire new directions in antibacterial research.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Multi drug resistant; Nanotechnology; Phytomedicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Islamic Azad University of Shahrekord Branch in Iran (IR.IAU.SHK.REC.1402). Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Doosti, A. Detection of T6SS secretory system and membrane purine involved in antibiotic resistance in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. 47–58 (2021).
-
- Piri Gharaghie, T., Beiranvand, S. & Hajimohammadi, S. Comparison of Antifungal effects of aquatic and alcoholic extract of Mentha pulegium L. with fluconazole on growth of Candida albicans. Dev. Biol.13 (2), 7–18 (2021).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

