Causal effects of retinol and vitamin D on tongue cancer risk: a mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39799281
- PMCID: PMC11725209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-05407-y
Causal effects of retinol and vitamin D on tongue cancer risk: a mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have indicated that retinol and vitamin D may be associated with the oncogenesis of tongue cancer. Therefore, we aimed to assess the causal relationships of retinol and vitamin D with the risk of tongue cancer using the two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) method.
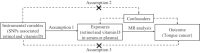
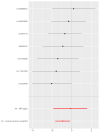
Methods: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to retinol, vitamin D and tongue cancer were obtained from the up-to-date genome-wide association study (GWAS) catalogue, which was screened for instrumental variables (IVs). We performed two-sample MR analyses and used inverse-variance weighted (IVW) as the primary method. Additionally, we used the MR-pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO) method, MR-Egger intercept analysis, Cochran's Q test and leave-one-out analysis to evaluate the sensitivity of MR.
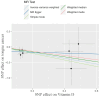
Results: The IVW method revealed that retinol was not significantly correlated with the risk of tongue cancer (OR = 0.8602; 95% CI = 0.4453-1.6617; P = 0.654). However, the causal relationship between vitamin D and the risk of tongue cancer was significant according to IVW (OR = 0.4003; 95% CI = 0.1868-0.8577; P = 0.019). The sensitivity analysis did not detect any significant horizontal pleiotropy or heterogeneity.
Conclusions: Given the limitations of this study, our MR study suggests that retinol is unlikely to influence the risk of tongue cancer, but vitamin D may decrease the risk of tongue cancer.
Keywords: Causal relationship; Mendelian randomization; Retinol; Tongue cancer; Vitamin D.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participants: The data of our MR study were obtained from the previous collected and published studies which had been ethically approved. No ethical approval was required in this study. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Causal association of serum vitamin D levels with urolithiasis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Eur J Nutr. 2024 Nov 30;64(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03553-1. Eur J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39614876
-
No causal association between serum vitamin D levels and bronchiectasis: A Mendelian randomization analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 6;103(49):e40824. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040824. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39654221 Free PMC article.
-
Mendelian randomization study investigating the relationship between nutrients and polycystic ovary syndrome.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025 Apr;169(1):198-205. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.16029. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 39569763 Review.
-
Serum Vitamin D Levels and Risk of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 24;13(3):e4746. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4746. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40008239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. Ca Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–36. - PubMed
-
- Rhodus NL, Kerr AR, Patel K. Oral cancer: leukoplakia, premalignancy, and squamous cell carcinoma. Dental Clin N Am. 2014;58:315–40. - PubMed
-
- Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471–4. - PubMed
-
- Mannelli G, Arcuri F, Agostini T, Innocenti M, Raffaini M, Spinelli G. Classification of tongue cancer resection and treatment algorithm. J Surg Oncol. 2018;117:1092–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

