Health utility scores of six common cancers in China measured by SF-6Dv2
- PMID: 39799326
- PMCID: PMC11725192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-025-02332-8
Health utility scores of six common cancers in China measured by SF-6Dv2
Abstract
Purpose: Given the recent update of SF-6Dv2, detailed data on utility scores for cancer patients by cancer type remain scarce in China and other regions, which limits the precision of cost-utility analyses (CUA) in cancer interventions. The aim of the study was to systematically evaluate utility scores of six common cancers in China measured using SF-6Dv2, and identify the potential factors associated with utility scores.
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional survey was conducted from August 2022 to December 2023. It recruited 896 cancer patients from three tertiary hospitals in China, including 270 with lung cancer, 96 with stomach cancer, 88 with liver cancer, 71 with oesophagus cancer, 142 with colorectum cancer, and 160 with breast cancer. The validated Simplified Chinese version of the SF-6Dv2 was used to calculate utilities based on the Chinese value set, and the utility values were described using the mean and standard deviation (SD). Participants' socio-demographic, behavioral and clinical characteristics were also obtained from the survey. Univariate and multivariate linear regression models were performed to explore the impact of these three categories of characteristics on utility scores derived from SF-6Dv2 for the total cancer patients and each cancer group.
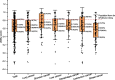
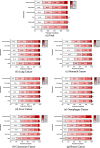
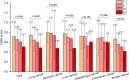
Results: The mean utility score was 0.66 (SD = 0.26) for the total cancer sample, 0.66 (SD = 0.25) for lung cancer, 0.75 (SD = 0.23) for stomach cancer, 0.69 (SD = 0.24) for liver cancer, 0.69 (SD = 0.24) for oesophagus cancer, 0.65 (SD = 0.31) for colorectum cancer, and 0.57 (SD = 0.24) for breast cancer. Multivariate linear regression analysis indicated that patients who were older, from larger families, under greater economic pressures, undergoing fewer health examinations, smoking, and in advanced cancer stages had lower utility scores in the total cancer sample (p<0.05), with variations observed across different cancer types.
Conclusions: This study is one of the first to apply the SF-6Dv2 to a heterogeneous group of cancer patients, providing evidence for conducting CUA with SF-6Dv2 across six common cancers in China. In addition, the study provides a basis for improving interventions for different cancer types.
Keywords: Cancer; China; Health utility; SF-6Dv2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The protocol of this study received approval from the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University (HMUIRB2023005). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical