Multi-disciplinary treatment of broncho-esophageal fistula in a high-risk single-lung patient
- PMID: 39799355
- PMCID: PMC11725186
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03287-5
Multi-disciplinary treatment of broncho-esophageal fistula in a high-risk single-lung patient
Abstract
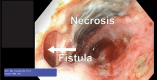
Background: A broncho-esophageal fistula (BEF) is a medical and surgical disaster. Treatment of BEF is often limited to palliative stent treatment that may migrate or cause erosions and tissue necrosis. Surgical repair of BEF is the only established definite treatment.
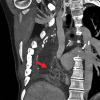
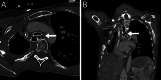
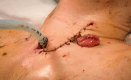
Case presentation: BEF presented in a 40-year-old female patient 8 years after curative treatment with pneumonectomy and radio-chemotherapy for advanced lung cancer. She had autoimmune comorbidity, a single lung, vocal cord paralysis and an extremely hostile thorax. Multi-disciplinary collaboration, close patient involvement and evaluation by the hospital medical ethics committee were key elements in the following treatment course. After temporary stent treatment, a carefully staged surgical marathon was performed: Veno-venous ECMO was established to secure oxygenation, and bilateral thoracotomy and laparotomy performed to access structures in the frozen mediastinum. After extensive thoracoplasty and high-risk dissection, esophagectomy was performed and the 20 × 35 mm bronchial defect repaired by bronchoplasty with a latissimus muscle flap. It was complicated by thrombotic occlusion of the upper venous system, repeated postoperative bleedings and critical illness neuropathy. The patient recovered and was discharged 150 days after surgery. Within 1-2 years bronchoscopy showed a smooth undiscernible bronchoplasty with a stable open left main bronchus. At 5 years the patient lives an independent life at home with her family.
Conclusions: Surgical treatment of BEF in an extremely complex patient may turn out successfully. It demands careful ethical considerations, comprehensive surgical strategy, multi-disciplinary teamwork, and shared decision making with the patient. The patient presented in this case report is closely followed up with good life quality after 5 years.
Keywords: Bronchial stent; Broncho-esophageal fistula; Bronchoplasty; Esophageal stent; Esophagectomy; Non-small lung cancer; Thoracoplasty; Tracheobronchial stent; Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: The patient has provided written informed consent for inclusion and publication of this case report. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Guarantor statement: RH is the guarantor of the content of the manuscript and takes responsibility for the integrity of the information and data presented.
Figures


References
-
- Griffo S, Stassano P, Iannelli G, Di Tommaso L, Cicalese M, Monaco M, Ferrante G. Benign bronchoesophageal fistula: report of four cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133(5):1378–9. - PubMed
-
- Miljeteig I, Johansson KA, Sayeed SA, Norheim OF. End-of-life decisions as bedside rationing. An ethical analysis of life support restrictions in an Indian neonatal unit. J Med Ethics. 2010;36(8):473–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

