Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress, Apoptosis, and Redox Signaling: Key Players in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 39799559
- PMCID: PMC11725306
- DOI: 10.1002/jbt.70133
Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress, Apoptosis, and Redox Signaling: Key Players in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
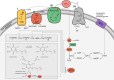
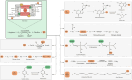
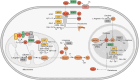
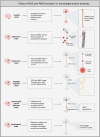
Neurodegenerative diseases are significant health concerns that have a profound impact on the quality and duration of life for millions of individuals. These diseases are characterized by pathological changes in various brain regions, specific genetic mutations associated with the disease, deposits of abnormal proteins, and the degeneration of neurological cells. As neurodegenerative disorders vary in their epidemiological characteristics and vulnerability of neurons, treatment of these diseases is usually aimed at slowing disease progression. The heterogeneity of genetic and environmental factors involved in the process of neurodegeneration makes current treatment methods inadequate. However, the existence of common molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of these diseases may allow the development of new targeted therapeutic strategies. Oxidative and nitrosative stress damages membrane components by accumulating ROS and RNS and disrupting redox balance. This process results in the induction of apoptosis, which is important in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases through oxidative stress. Studies conducted using postmortem human samples, animal models, and cell cultures have demonstrated that oxidative stress, nitrosative stress, and apoptosis are crucial factors in the development of diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Multiple Sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Huntington's disease. The excessive production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, elevated levels of free radicals, heightened mitochondrial stress, disturbances in energy metabolism, and the oxidation and nitrosylation of cellular macromolecules are recognized as triggers for neuronal cell death. Challenges in managing and treating neurodegenerative diseases require a better understanding of this field at the molecular level. Therefore, this review elaborates on the molecular mechanisms by which oxidative and nitrosative stress are involved in neuronal apoptosis.
Keywords: Oxidative stress; apoptosis; molecular mechanisms; neurodegenerative diseases; nitrosative stress; redox signaling.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fereshtehnejad S. M., Vosoughi K., Heydarpour P., et al., “Burden of Neurodegenerative Diseases in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 1990‐2016: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016,” European Journal of Neurology 26, no. 10 (2019): 1252–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

