Proteomic signature of HIV-associated subclinical left atrial remodeling and incident heart failure
- PMID: 39800750
- PMCID: PMC11725572
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55911-0
Proteomic signature of HIV-associated subclinical left atrial remodeling and incident heart failure
Abstract
People living with HIV are at higher risk of heart failure and associated left atrial remodeling compared to people without HIV. Mechanisms are unclear but have been linked to inflammation and premature aging. Here we obtain plasma proteomics concurrently with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in two independent study populations to identify parallels between HIV-related and aging-related immune dysfunction that could contribute to atrial remodeling and clinical heart failure. We discover a plasma proteomic signature that may in part reflect or contribute to HIV-associated atrial remodeling, many features of which are associated with older age and time to incident heart failure among an independent community-based cohort without HIV. This proteomic profile was statistically enriched for immune checkpoint proteins, tumor necrosis factor signaling, ephrin signaling, and extracellular matrix organization, identifying possible shared pathways in HIV and aging that may contribute to risk of heart failure.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: T.T.B. has served as a consultant to Gilead Sciences, Merck, ViiV Healthcare, and Janssen. F.J.P. has served as a consultant and/or on the Speakers Bureau for Gilead Sciences, Merck, ViiV Healthcare, and EMD Serono. S.S.R. is a consultant to the NHLBI TOPMed Administrative Coordinating Center (Westat). J.S.B. is an advisor to Dextera Biosciences, Inc. and is a founder of and advisor to Neochromosome, Inc. and its parent company Opentrons Labworks, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
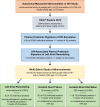


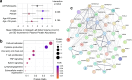
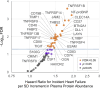
Update of
-
Proteomic Signature of HIV-Associated Subclinical Left Atrial Remodeling and Incident Heart Failure.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 14:2024.02.13.24302797. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.13.24302797. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 12;16(1):610. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55911-0. PMID: 38405757 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 HL166770/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI094189/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN2682015000031, HSN26800004, HHSN268201600034I/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIAAG000297/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000297/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DA036297/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL146193, U01-HL146240, U01-HL146205/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- HL007227/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- K24 AI120834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126552/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007227/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23HL166770-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL146201/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

