Chronic enrichment affects nitrogen removal in tidal freshwater river and estuarine creek sediments
- PMID: 39801377
- PMCID: PMC11893282
- DOI: 10.1002/jeq2.20674
Chronic enrichment affects nitrogen removal in tidal freshwater river and estuarine creek sediments
Abstract
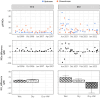
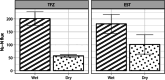
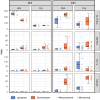
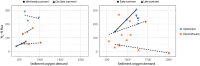
Population growth in coastal areas increases nitrogen inputs to receiving waterways and degrades water quality. Wetland habitats, including floodplain forests and marshes, can be effective nitrogen sinks; however, little is known about the effects of chronic point source nutrient enrichment on sediment nitrogen removal in tidally influenced coastal systems. This study characterizes enrichment patterns in two tidal systems affected by wastewater treatment facility (WWTF) effluent and assesses the impact on habitat nitrogen removal via denitrification. We collected intact sediment cores from prevalent habitats in a tidal freshwater river (TFZ; swamp forest) and a tidal estuarine creek system (EST; salt marsh) upstream and downstream of a WWTF outfall, and quantified dissolved gas fluxes across the sediment-water interface during wet conditions in early summer and dry conditions in late summer. Data collected during two synoptic water quality monitoring campaigns complimented laboratory experiments to provide environmental context for biogeochemical processing. The two systems exhibited different enrichment patterns such that the river-dominated TFZ system was characterized by consistently elevated nitrate + nitrite concentrations downstream of the WWTF, whereas precipitation and tidal influence affected nutrient distributions in the EST creek. Downstream sediments in TFZ exhibit an apparent saturation response, while upstream rates may be limited by other factors, such as labile organic matter availability. In contrast, downstream sediments in EST denitrify at higher rates than upstream during wet conditions that may enhance transport of effluent. This work provides information on ecosystem functioning in human-influenced environments and can be of use in developing nature-based solutions, such as water treatment wetlands, for nitrogen removal.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Environmental Quality published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nutrient distribution and nitrate processing in a mangrove tidal creek affected by submarine groundwater discharge (SGD).Mar Pollut Bull. 2025 Mar;212:117575. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2025.117575. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Mar Pollut Bull. 2025. PMID: 39824124
-
Nitrogen, sulfur, iron, and microbial communities co-shape the seasonal biogeochemical behaviors of As and Sb in coastal tidal flat wetlands associated with rivers.J Hazard Mater. 2025 Feb 15;484:136730. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136730. Epub 2024 Dec 1. J Hazard Mater. 2025. PMID: 39637813
-
Assessment and monitoring of nutrient loading in the sediments of tidal creeks receiving shrimp farm effluent in Quang Ninh, Vietnam.Environ Monit Assess. 2013 Oct;185(10):8715-31. doi: 10.1007/s10661-013-3207-2. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Environ Monit Assess. 2013. PMID: 23616080
-
Nitrous oxide fluxes in estuarine environments: response to global change.Glob Chang Biol. 2015 Sep;21(9):3219-45. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12923. Epub 2015 May 12. Glob Chang Biol. 2015. PMID: 25752934 Review.
-
Assessing the risk of utilizing tidal coastal wetlands for wastewater management.J Environ Manage. 2019 Apr 15;236:269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.082. Epub 2019 Feb 6. J Environ Manage. 2019. PMID: 30738297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boets, P. , Dillen, A. , Mertens, J. , Vervaeke, B. , Van Thuyne, G. , Breine, J. , Goethals, P. , & Poelman, E. (2021). Do investments in water quality and habitat restoration programs pay off? An analysis of the chemical and biological water quality of a lowland stream in the Zwalm River basin (Belgium). Environmental Science & Policy, 124, 115–124. 10.1016/j.envsci.2021.06.017 - DOI
-
- Boustany, R. G. , Crozier, C. R. , Rybczyk, J. M. , & Twilley, R. R. (1997). Denitrification in a south Louisiana wetland forest receiving treated sewage effluent. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 4(1), 273–283.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

