APH Inhibitors that Reverse Aminoglycoside Resistance in Enterococcus casseliflavus
- PMID: 39801466
- PMCID: PMC12005471
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202400842
APH Inhibitors that Reverse Aminoglycoside Resistance in Enterococcus casseliflavus
Abstract
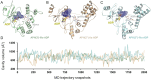
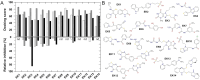
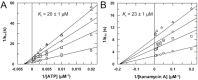
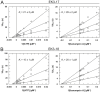
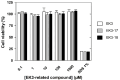
Aminoglycoside-phosphotransferases (APHs) are a class of bacterial enzymes that mediate acquired resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Here we report the identification of small molecules counteracting aminoglycoside resistance in Enterococcus casseliflavus. Molecular dynamics simulations were performed to identify an allosteric pocket in three APH enzymes belonging to 3' and 2'' subfamilies in which we then screened, in silico, 12,000 small molecules. From a subset of only 14 high-scored molecules tested in vitro, we identified a compound, named here EK3, able to non-competitively inhibit the APH(2'')-IVa, an enzyme mediating clinical gentamicin resistance. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) exploration of this hit compound allowed us to identify a molecule with improved enzymatic inhibition. By measuring bacterial sensitivity, we found that the three best compounds in this series restored bactericidal activity of various aminoglycosides, including gentamicin, without exhibiting toxicity to HeLa cells. This work not only provides a basis to fight aminoglycoside resistance but also highlights a proof-of-concept for the search of allosteric modulators by using in silico methods.
Keywords: Allostery; Antibiotic resistance; Inhibitors; Molecular docking; Virtual screening.
© 2025 The Authors. ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-guided optimization of protein kinase inhibitors reverses aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance.Biochem J. 2013 Sep 1;454(2):191-200. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130317. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23758273 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance and inhibition mechanism of novel aminoglycoside phosphotransferase APH(5) from B. subtilis subsp. subtilis strain RK.Braz J Microbiol. 2019 Oct;50(4):887-898. doi: 10.1007/s42770-019-00132-z. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Braz J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31401782 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic characterization and molecular docking of novel allosteric inhibitors of aminoglycoside phosphotransferases.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Jan;1861(1 Pt A):3464-3473. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27640112
-
Prospects for circumventing aminoglycoside kinase mediated antibiotic resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Jun 25;3:22. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00022. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23805415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets for design of novel inhibitors to circumvent aminoglycoside resistance.Curr Drug Targets. 2005 May;6(3):353-61. doi: 10.2174/1389450053765860. Curr Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 15857293 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Safety Assessment of Ralstonia eutropha H16 for Food Applications: Integrating Genomic, Phenotypic, and Toxicological Analyzes.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 6;13(6):1323. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061323. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572211 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

