The Investing Layer of the Deep Cervical Fascia: An Alternative Site for Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular Nerve Block - A Cadaveric Anatomical Study
- PMID: 39801553
- PMCID: PMC11717074
- DOI: 10.4103/jmu.jmu_121_23
The Investing Layer of the Deep Cervical Fascia: An Alternative Site for Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular Nerve Block - A Cadaveric Anatomical Study
Abstract
Background: It is very well known that the supraclavicular nerve (SCN) which occupies the inferior part of the superficial cervical plexus basically originates from the ventral rami of C2-C4, then travels caudally into the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia (IL-DCF) alternatively termed the "prevertebral fascia."
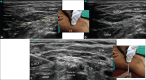
Methods: This cadaveric study (a total of 6 soft-embalmed cadavers and bilateral dissections, i.e. 12 specimens) intended to ascertain the location of SCN within the layers of the IL-DCF. We hypothesized that ultrasonography identification of SCN within the IL-DCF and needle tip positioned between the layers of IL-DCF provide an alternative site for the blockade of the SCN.
Results: After dissection, we described a compact double-layered IL-DCF hosting the SCNs and a specific topographic arrangement at the C4 root with SCN lateral and C4 branches of the phrenic nerve medial to the C4.
Conclusion: We recommend another alternative site for the SCN block at a site in the compact double layer of IL-DCF. We conclude that a caudal site at the exit of SCN from the IL-DCF would be appropriate to perform the intervention.
Keywords: Cadaver; deep cervical fascia; dissection; supraclavicular nerve; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Medical Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang JC, Hsu PC, Wang KA, Wu WT, Chang KV. comparative effectiveness of corticosteroid dosages for ultrasound-guided glenohumeral joint hydrodilatation in adhesive capsulitis: A randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104:745–52. - PubMed
-
- Wu WT, Lin CY, Shu YC, Chen LR, Özçakar L, Chang KV. Subacromial motion metrics in painful shoulder impingement: A dynamic quantitative ultrasonography analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104:260–9. - PubMed
-
- Chang KV, Lin CP, Hung CY, Özçakar L, Wang TG, Chen WS. Sonographic nerve tracking in the cervical region: A pictorial essay and video demonstration. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;95:862–70. - PubMed
-
- Diwan S, Nair A, Sermeus LA, Patil AA, Attarde DS. Low-volume local anesthetics for C5 and supraclavicular nerve blocks for mid and lateral clavicle surgery: A case series. A A Pract. 2020;14:e01322. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
