Sphingosylphosphorylcholine Promotes Th9 Cell Differentiation Through Regulation of Smad3, STAT5, and β-Catenin Pathways
- PMID: 39801737
- PMCID: PMC11711130
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e45
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine Promotes Th9 Cell Differentiation Through Regulation of Smad3, STAT5, and β-Catenin Pathways
Abstract
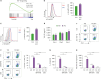
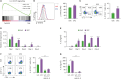
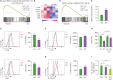
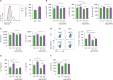
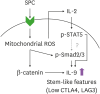
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) is one of sphingomyelin-derived sphingolipids. SPC levels are increased in ascitic fluids of ovarian cancer patients and stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis (AD) patients. SPC has antitumor activity against several cancer cells by reducing proliferation and migration and increasing apoptosis in vitro. SPC can also cause scratching, potentially exacerbating symptoms of AD. However, the role of SPC in modulating immune responses, particularly in the differentiation of Th9 cells, which carry the most powerful antitumor activity among CD4+ T cells, has yet to be investigated. In this study, we found that SPC is another inducer of Th9 cell differentiation by replicating TGF-β. SPC upregulated Smad3, STAT5, and β-catenin signaling pathways. Increased Smad3 and STAT5 signaling pathways by SPC promoted the differentiation of Th9 cells and increased β-catenin signaling pathway resulted in a less-exhausted, memory-like phenotype of Th9 cells. Increased Smad3, STAT5 and β-catenin signaling pathways by SPC were mediated by increased mitochondrial ROS. These results suggest that SPC is an important endogenous inducer of Th9 cell differentiation and may be one of the targets for treating Th9-related diseases, and that enhancing Th9 differentiation by SPC may be helpful in adoptive T cell therapy for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Beta-catenin; Interleukin-9; Reactive oxygen species; STAT5 transcription factor; Smad3 protein; Sphingosylphosphorylcholine.
Copyright © 2024. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Ji Cheol Kim and Yoe-Sik Bae have pending patents related to this discovery. The other authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Schmitt E, Germann T, Goedert S, Hoehn P, Huels C, Koelsch S, Kühn R, Müller W, Palm N, Rüde E. IL-9 production of naive CD4+ T cells depends on IL-2, is synergistically enhanced by a combination of TGF-beta and IL-4, and is inhibited by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1994;153:3989–3996. - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, Martin B, Wilhelm C, Stockinger B. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1341–1346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

