Emerging trends and new developments in global research on artemisinin and its derivatives
- PMID: 39801992
- PMCID: PMC11720899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41086
Emerging trends and new developments in global research on artemisinin and its derivatives
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization recommends the use of artemisinin (ART) and its derivatives for malaria treatment. Furthermore, these compounds exhibit encouraging pharmacological effects for the treatment of several diseases. Nevertheless, ongoing antimalarial treatment efforts have been significantly hindered by the emergence of drug resistance. A systematic evaluation and analysis of relevant studies may yield insights to help resolve this dilemma and reveal options for future research.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to provide researchers with a comprehensive synopsis of the advancements made in the study of ART and its significant derivatives, as well as to visually present the data and provide insightful observations that can inform subsequent investigations in this domain.
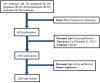
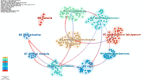
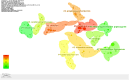
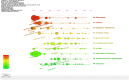
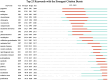
Methods: We searched the Web of Science Core Collection for relevant studies published by December 31, 2023. The research hotspots and frontiers pertinent to this field in terms of countries, institutions, authors, journals, references, and keywords were ascertained through scientometric analysis via CiteSpace software.
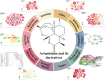
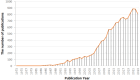
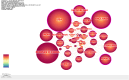
Results: This study included an extensive assemblage of 12,985 data points, and the findings suggest that ART and its derivatives have garnered considerable interest among scientists. Prolonged international collaboration has fostered progress in this research field. "Antimalarials," "synthesis," "drug resistance," and "Plasmodium vivax" are areas of intense research. Potential areas for future investigations may include "proliferation," "oxidative stress," "pathways," and "mechanisms."
Conclusion: This study offers a comprehensive compendium of the developments and trends in the relevant research field over the past fifty years. Since pharmaceutical drug synthesis can influence both drug efficacy and cost-effectiveness, ongoing efforts to improve drug synthesis are warranted. Although the advent of novel therapeutic approaches has partially mitigated drug resistance, further investigations into the underlying mechanisms are needed. While better treatments for malaria have been developed, the therapeutic potential of ART and its derivatives for numerous additional important diseases is also possible, and future research in this area can lead to dramatic improvements in health.
Keywords: Artemisinin; CiteSpace; Derivatives; Malaria; Scientometric analysis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bibliometric analysis of antimalarial drug resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 12;14:1270060. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1270060. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38410722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Combined antimalarial therapy using artemisinin].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):85-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305693 Review. Italian.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Knowledge domain and emerging trends in multimorbidity and frailty research from 2003 to 2023: a scientometric study using citespace and VOSviewer.Health Econ Rev. 2023 Oct 10;13(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13561-023-00460-9. Health Econ Rev. 2023. PMID: 37815722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frontiers and hotspots of high-intensity interval exercise in children and adolescents: text mining and knowledge domain visualization.Front Physiol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1330578. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1330578. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38510943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO . 2023. World Malaria Report 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

