Therapeutic potential of seaweeds and their biofabricated nanoparticles in treating urolithiasis: A review
- PMID: 39802010
- PMCID: PMC11720914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41132
Therapeutic potential of seaweeds and their biofabricated nanoparticles in treating urolithiasis: A review
Abstract
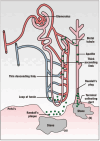
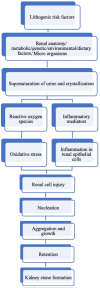
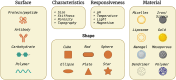
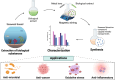
Urolithiasis affects a significant portion of the global population, causing discomfort and pain. Unfortunately, effective drugs to treat this disorder are currently unavailable due to multiple mechanisms and an incomplete understanding of its causes. Consequently, drugs with multiple targets could be a safer and more effective remedy for treating urolithiasis. Moreover, the current treatment options are expensive and come with a risk of complications and stone recurrence. Therefore, an alternative treatment that can prevent stone recurrence and reduce associated symptoms is necessary. Seaweeds are a rich source of beneficial metabolites, like antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and enzyme-inhibitory properties. Advances in nanotechnology hold great promise for improving the therapeutic potential of these metabolites. However, the use of nanoparticles for treating urolithiasis has yet to be explored well, and only a few reports exist on the use of terrestrial plant-based nanoparticles. This review examines the therapeutic properties of seaweed bioactive compounds and their possible applications in treating urolithiasis. We propose that seaweeds could be an excellent source of essential dietary minerals and other bioactive compounds with multiple targets to treat renal calculus naturally. Additionally, the review highlights the potential of nanomedicine in treating urolithiasis, proposing seaweed-based nanoparticles as a promising treatment option.
Keywords: Inflammation; Nanomedicine; Nanoparticles; Oxidative stress; Seaweeds; Urolithiasis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
“The authors declare no competing interests.”
Figures
References
-
- Mathur V., Rajvansh A. National case study; India: 2001. The Integration of Biodiversity into National Environmental Assessment Procedures. UNDP/UNEP/GEF BPSP- Komex.
-
- Anis M., Ahmed S., Hasan M.M. Algae as nutrition, medicine and cosmetic: the forgotten history, present status and future trends. World J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2017;6:1934–1959. doi: 10.20959/wjpps20176-9447. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

