Can Digital Rectal Examination Identify the Subtype of Dyssynergic Disorders as Well as High Resolution Anorectal Manometry?
- PMID: 39802135
- PMCID: PMC11724330
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.70097
Can Digital Rectal Examination Identify the Subtype of Dyssynergic Disorders as Well as High Resolution Anorectal Manometry?
Abstract
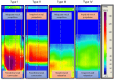
Background and aims: Diagnosing dyssynergic disorders (DD) often requires 3D high-definition anorectal manometry (3D-HRAM), raising concerns about cost, availability, and delayed referral. Digital rectal examination (DRE) offers a reliable, cost-effective alternative for DD diagnosis. This study aimed to assess DRE's capability to classify DD patients into the four subtypes outlined in Rao's classification.
Methods: This retrospective monocentric study involved patients diagnosed with DD through 3D-HRAM. After initial 3D-HRAM performed by one physician, patients underwent a clinical examination, including DRE by a second senior clinician blinded to DD subtypes. Statistical tests measured the correlation between DRE and HRAM in classifying the four DD subtypes.
Results: The study included 200 patients, revealing commendable overall agreement between DRE and 3D-HRAM (Kappa = 0.658). For subtype diagnosis, correlation was substantial for Subtypes I, II, and IV (0.679, 0.741, 0.649, respectively) and moderate for Subtype III (Kappa = 0.325).
Conclusion: DRE demonstrates satisfactory performance in diagnosing the four subtypes of DD. Enhanced training in DRE, emphasizing functional information, has the potential to reduce reliance on additional tests, thereby mitigating economic and organizational impacts.
Keywords: DRE; HRAM; dyssynergic disorders; subtypes.
© 2025 The Author(s). JGH Open published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Heitmann P. T., Vollebregt P. F., Knowles C. H., Lunniss P. J., Dinning P. G., and Scott S. M., “Understanding the Physiology of Human Defaecation and Disorders of Continence and Evacuation,” Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology and Hepatology 18 (2021): 751–769, 10.1038/s41575-021-00487-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun S. X., Dibonaventura M., Purayidathil F. W., et al., “Impact of Chronic Constipation on Health‐Related Quality of Life, Work Productivity, and Healthcare Resource Use: An Analysis of the National Health and Wellness Survey,” Digestive Diseases and Sciences 56 (2011): 2688–2695, 10.1007/s10620-011-1639-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources