Microneedles as a Promising Technology for Disease Monitoring and Drug Delivery: A Review
- PMID: 39802146
- PMCID: PMC11718548
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmaterialsau.4c00125
Microneedles as a Promising Technology for Disease Monitoring and Drug Delivery: A Review
Abstract
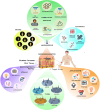
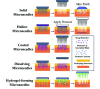
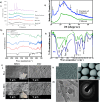
The delivery of molecules, such as DNA, RNA, peptides, and certain hydrophilic drugs, across the epidermal barrier poses a significant obstacle. Microneedle technology has emerged as a prominent area of focus in biomedical research because of its ability to deliver a wide range of biomolecules, vaccines, medicines, and other substances through the skin. Microneedles (MNs) form microchannels by disrupting the skin's structure, which compromises its barrier function, and facilitating the easy penetration of drugs into the skin. These devices enhance the administration of many therapeutic substances to the skin, enhancing their stability. Transcutaneous delivery of medications using a microneedle patch offers advantages over conventional drug administration methods. Microneedles containing active substances can be stimulated by different internal and external factors to result in the regulated release of the substances. To achieve efficient drug administration to the desired location, it is necessary to consider the design of needles with appropriate optimized characteristics. The choice of materials for developing and manufacturing these devices is vital in determining the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drug delivery. This article provides the most recent update and overview of the numerous microneedle systems that utilize different activators to stimulate the release of active components from the microneedles. Further, it discusses the materials utilized for producing microneedles and the design strategies important in managing the release of drugs. An explanation of the commonly employed fabrication techniques in biomedical applications and electronics, particularly for integrated microneedle drug delivery systems, is discussed. To successfully implement microneedle technology in clinical settings, it is essential to comprehensively assess several factors, such as biocompatibility, drug stability, safety, and production cost. Finally, an in-depth review of these criteria and the difficulties and potential future direction of microneedles in delivering drugs and monitoring diseases is explored.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 13;15(1):277. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010277. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedles in diagnostic, treatment and theranostics: An advancement in minimally-invasive delivery system.Biomed Microdevices. 2021 Dec 8;24(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s10544-021-00604-w. Biomed Microdevices. 2021. PMID: 34878589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metallic microneedles with interconnected porosity: A scalable platform for biosensing and drug delivery.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:401-411. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30201432
-
Innovative freeze-drying technique in the fabrication of dissolving microneedle patch: Enhancing transdermal drug delivery efficiency.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Nov;14(11):3112-3127. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01531-y. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38431532
-
Microneedles and their applications.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2011 May;5(2):95-132. doi: 10.2174/187221111795471445. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2011. PMID: 21453248 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
