Effectiveness of Balanced Electrolyte Solution vs Normal Saline in the Resuscitation of Adult Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39802248
- PMCID: PMC11719558
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24861
Effectiveness of Balanced Electrolyte Solution vs Normal Saline in the Resuscitation of Adult Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim and background: Fluid resuscitation is the first-line treatment for patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). However, the optimal choice of resuscitative fluid remains controversial. This study aims to evaluate the impact of balanced electrolyte solution (BES) compared to 0.9% sodium chloride (NS) on various physiological and clinical outcomes in adult DKA patients.
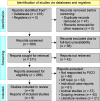
Materials and methods: An extensive search of electronic databases, including Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, was conducted to select studies that directly compared BES and NS in adult DKA patients. This systematic review and meta-analysis included nine studies, comprising both randomized controlled trials and retrospective studies. Combined estimates were expressed as mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The primary outcomes were time to resolution of DKA and length of hospital stay. The secondary outcomes were post-resuscitation chloride and bicarbonate levels and adverse events.
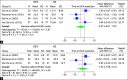
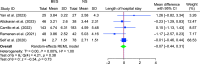
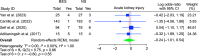
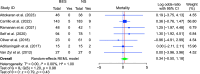
Results: No significant difference was observed between BES and NS in the time to DKA resolution (MD: -1.63; 95% CI: -7.66-4.41; p = 0.60) or length of hospital stay (MD: -0.07; 95% CI: -0.44-0.31; p = 0.73). However, BES resulted in significantly higher post-resuscitation bicarbonate levels (MD: 1.63; 95% CI: 0.86-2.39; p < 0.001) and lower post-resuscitation chloride levels (MD: -2.37; 95% CI: -3.56 to -1.19; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The use of BES is associated with improved post-resuscitation electrolyte balance and preventing hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis in DKA patients. While BES may offer some biochemical advantages, both BES and NS are safe for treating DKA.
How to cite this article: Gupta P, Nasa P, Shahabdeen SM. Effectiveness of Balanced Electrolyte Solution vs Normal Saline in the Resuscitation of Adult Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Indian J Crit Care Med 2025;29(1):65-74.
Keywords: Balanced electrolyte solution; Diabetic ketoacidosis; Fluid resuscitation; Metabolic acidosis; Normal saline; Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2025; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: NoneConflict of interest: None
Figures





References
-
- Lizzo JM, Goyal A, Gupta V. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis. 2023. In: StatPearls [Internet].
-
- Almazrouei R, Siddiqua AR, Alnuaimi M, Al-Shamsi S, Govender R. Clinical and biochemical characteristics of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes at a tertiary hospital in the United Arab Emirates. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2022;3:918253. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2022.918253. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gosmanov AR, Kitabchi AE. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, . South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc; 2000. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. In:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279146/ editors. Endotext [Internet] Available from:
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
